- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]
1. The most common cause of odontalgia is
a) Dental caries
b) Pulpitis
c) Root fracture
d) Periodontitis
ANSWER b
- A odontalgia is any pain or soreness within or around a tooth, indicating inflammation and possible infection.
- A odontalgia may feel like a sharp pain or a dull ache. The tooth may be sensitive to pressure, heat, cold, or sweets.
Toothaches may result from any of a number of causes:
- Traumatic injury
- Exposed tooth root Tooth decay food wedged (dental caries) between teeth or trapped below the inflammation of gum line the tooth pulp
- Pressure (pulpitis)
- Cavities.
- Abscessed tooth.
- Cracked tooth.
- A damaged dental restoration (like a filling or crown).
- Teeth grinding or clenching (bruxism).
- Gum disease.
2. The phenomenon by which bacteria circulating in blood accumulate at the site of pulpal inflammation is called as
a) Chemotaxis
b) Retrograde pulpitis
c) Anachoretic pulpitis
d) Aerodontalgia
ANSWER c
Anachoretic Pulpitis:
- It is the type of pulpitis when the pulpal inflammation is seen due to the bacteria entering into the blood stream through a Chemical or Mechanical injury to the pulp.
- In general Anachoresis is seen when substance like bacteria, pigments, dyes, metallic substances, foreign proteins and other foreign particles enter the blood stream infecting the pulp tissue.
- This phenomenon is due to increased capillary permeability in the particular area.
3. The lateral radicular cyst arises from
a) Cell rests of Malassez
b) Cell rests of Serres
c) Overlying oral epithelium
d) Dental lamina
ANSWER a
It usually arises from epithelial cell rests of Malassez existing within the periodontal ligament in response to necrosed pulp/trauma-induced inflammation.
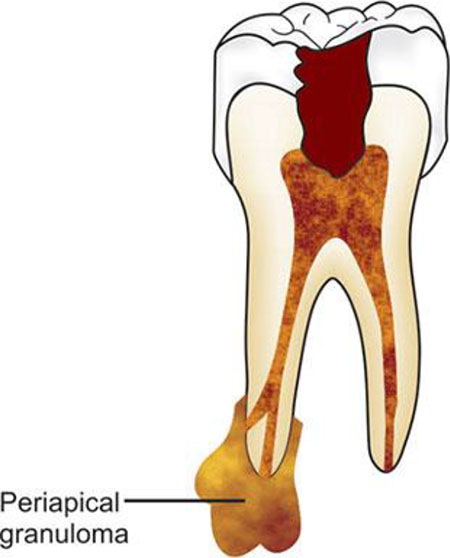
4. Chronic apical periodontitis is another name of
a) Phoenix abscess
b) Periapical abscess
c) Periapical granuloma
d) Periapical cyst
ANSWER c
- A periapical granuloma is a relatively common lesion or growth that develops around the tip of a tooth’s root.
- It consists of a proliferating mass of granulation tissue (new tissue that forms on a wound) and bacteria that forms in response to dead tissue in the pulp chamber of the tooth
- Periapical granuloma is one of the most common of all sequelae of pulpitis.
- It is essentially a localised mass of chronic granulation tissue formed in response to the infection. The involved tooth is sensitive to percussion
- Periapical granuloma, also referred to as chronic apical periodontitis, is a defensive reaction in response to bacterial infection within the pulp chamber which spreads to the root apex
5. Which amongst the following is not a predisposing factor of osteomyelitis?
a) Trauma to bone
b) Radiation damage to bone
c) Paget’s disease
d) Fibrous dysplasia
ANSWER d
- Osteomyelitis means an infection of bone, which can either be acute or chronic
Some of the risk factors that may increase a person’s susceptibility to osteomyelitis include:
- Long term skin infections.
- Inadequately controlled diabetes.
- Poor blood circulation (arteriosclerosis).
- Risk factors for poor blood circulation, which include high blood pressure, cigarette smoking, high blood cholesterol and diabetes.
- Immune system deficiency.
- Radiation damage
- Prosthetic joints.
- The use of intravenous drugs.
- Sickle cell anaemia.
- Cancer.





