- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]
Alkaptonuria, also called black urine disease, alcaptonuria, and black bone disease, is one of 4 disorders originally defined as an inborn error of metabolism by Archibald Garrod in his Croonian Lectures of 1902.
The hallmark of the disease is passage of urine that becomes black when left standing.
CAUSE
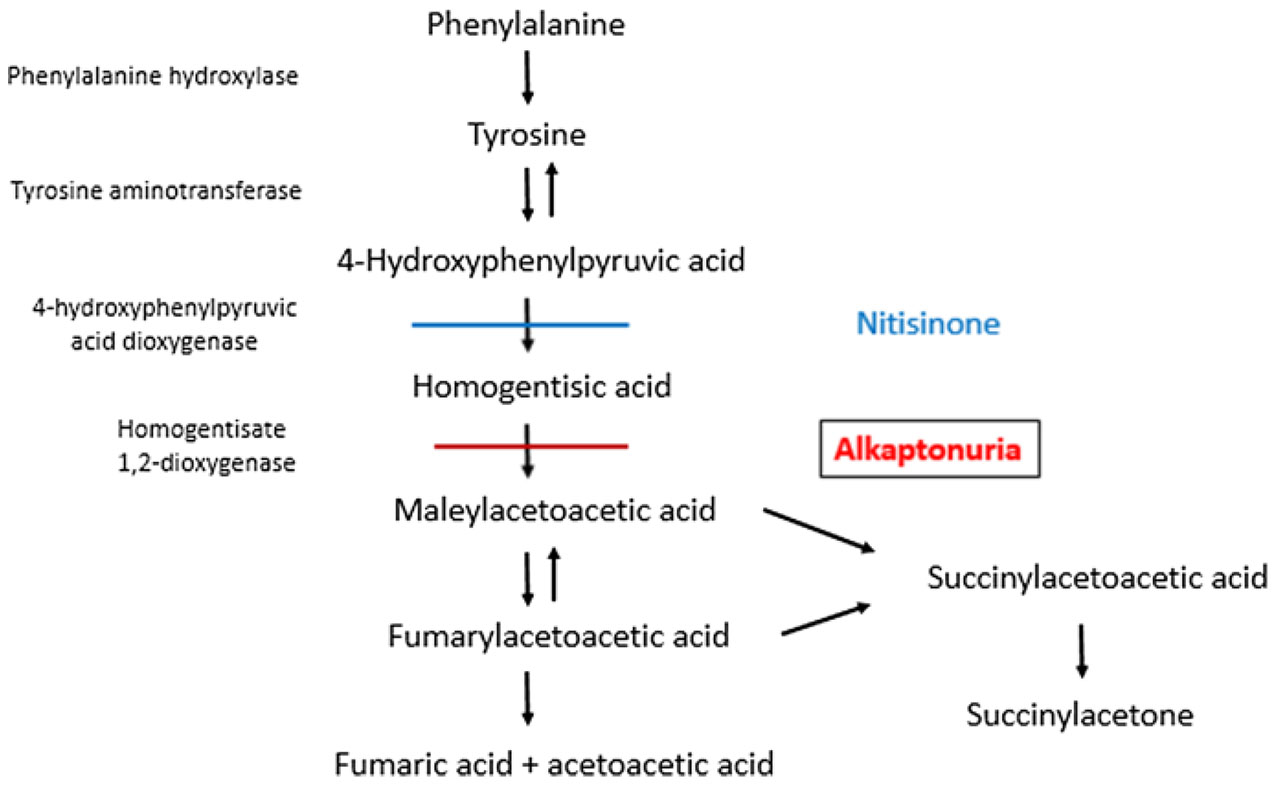
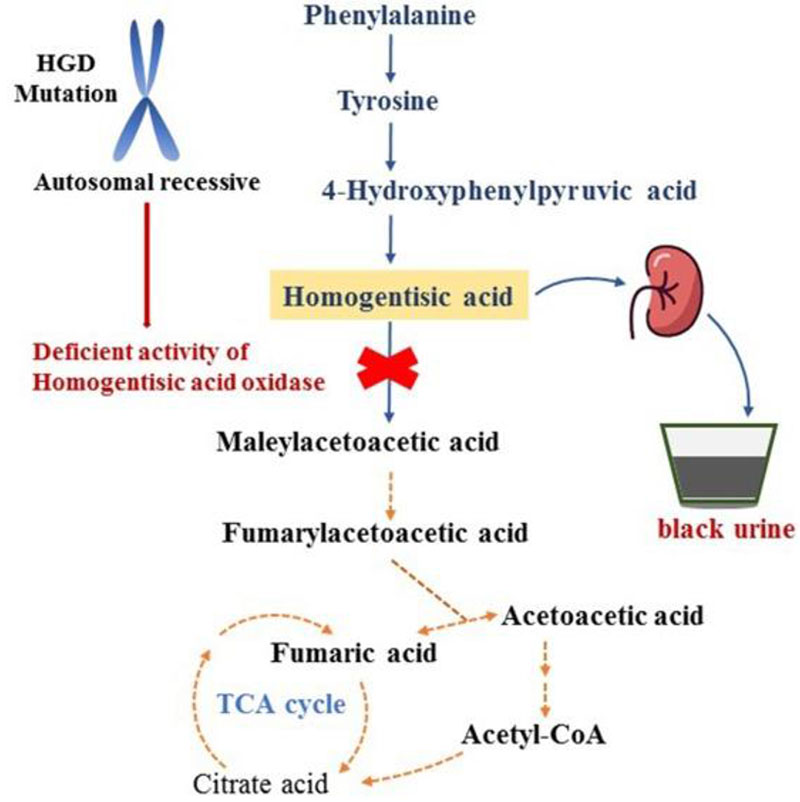
- Mutations in the HGD gene cause alkaptonuria.
- The HGD gene provides instructions for making an enzyme called homogentisate oxidase.
- This enzyme helps break down the amino acids phenylalanine and tyrosine, which are important building blocks of proteins.
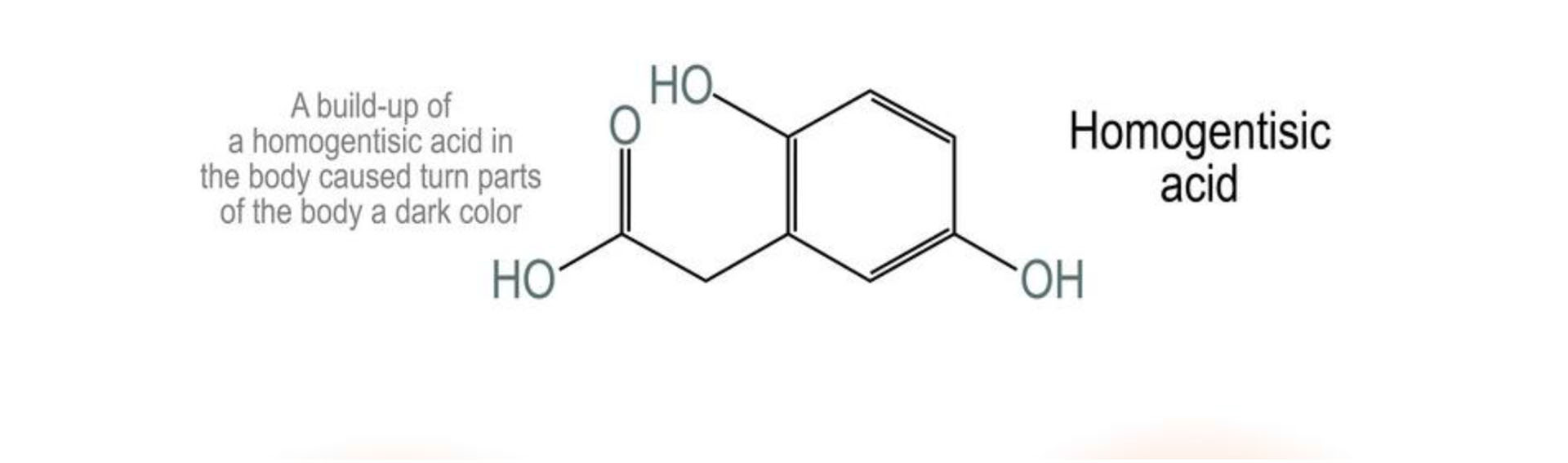
- Mutations in the HGD gene impair the enzyme's role in this process. As a result, a substance called homogentisic acid, which is produced as phenylalanine and tyrosine are broken down, accumulates in the body.
- Homogentisic acid is also excreted in urine, making the urine turn dark when exposed to air.
INHERITANCE
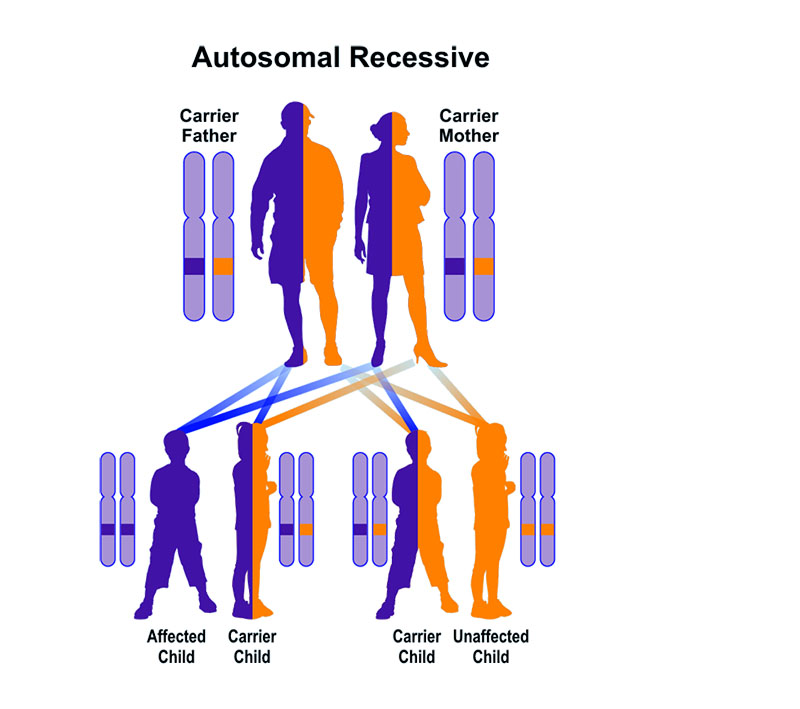
Alkaptonuria is inherited as an autosomal recessive trait
The risk to have a child who is a carrier like the parents is 50 percent with each pregnancy. The chance for a child to receive normal genes from both parents and be genetically normal for that particular trait is 25 percent. The risk is the same for males and females.
Garrod identified a familial pattern of inheritance and concluded that an inherited biochemical abnormality must result in the passage of an abnormal intermediate in the urine
SIGN AND SYMPTOMS
Patients with alkaptonuria are asymptomatic as children or young adults, but their urine may turn brown or even inky black if collected and left exposed to open air.
| Joints and bones | After 30s patient experience pain. Lower back pain and stiffness, followed by knee, hip and shoulder pain. These are similar to the early symptoms of osteoarthritis. Bone mineral density may be affected, increasing the risk of bone fractures, and rupture of tendons and muscles may. Homogentisic acid accumulates in other connective tissue including tendons and ligaments and even bone. Ochronosis is a metabolic arthropathy caused by alkaptonuria with excess homogentistic acid deposited in the joints. |
 |
| Eyes | Brown or black spots on the whites of their eyes | 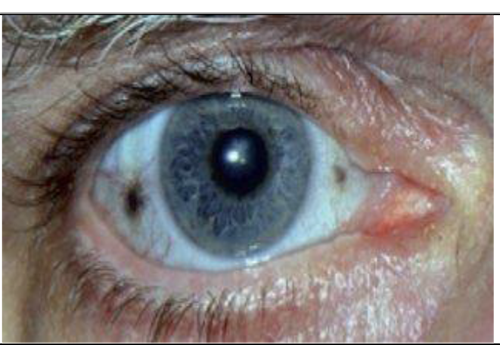 |
| Ear | Thickening of ear cartilage. The cartilage may also look blue, grey or black. This is called ochronosis. The earwax may be black or reddish-brown. |
 |
| Skin and nails | Discoloured sweat, which can
stain cloth
Some people to have blue or
black speckled areas of skin.
Nails may also turn a bluish or
brownish colour. The skin colour changes are most obvious on areas exposed to the sun and where sweat glands are found – the cheeks, forehead, armpits and genital area |
 |
| Breathing issue | The involvement of the spinal joints leads to reduced movement of the rib cage and can affect breathing | |
| Kidney | Developing kidney stones exists Changing of urine color when exposed in air |  |
| Salivary gland | Sialolithiasis can occur | |
| Heart | May develop due to the accumulation of homogentisic acid within the aortic or mitral valves. This accumulation causes thickening of the valves and narrowing (stenosis) of the openings of the valves. Calcification of the small blood vessels that supply blood and oxygen to the heart (coronary blood vessels) may also occur. |
DIAGNOSIS
It can be confirmed or excluded by collecting urine for 24 hours and determining the amount of homogentisic acid by means of chromatography.
TREATMENT
- Alkaptonuria is a lifelong condition.
- Nitisinone reduces the level of homogentisic acid in the body.
- Main treatment attempts have focused on preventing ochronosis through the reduction of accumulating homogentisic acid. Such commonly recommended treatments include large doses of ascorbic acid (vitamin C) or dietary restriction of amino acids phenylalanine and tyrosine.
- Another modality of treatment is done according to the symptoms.