- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]
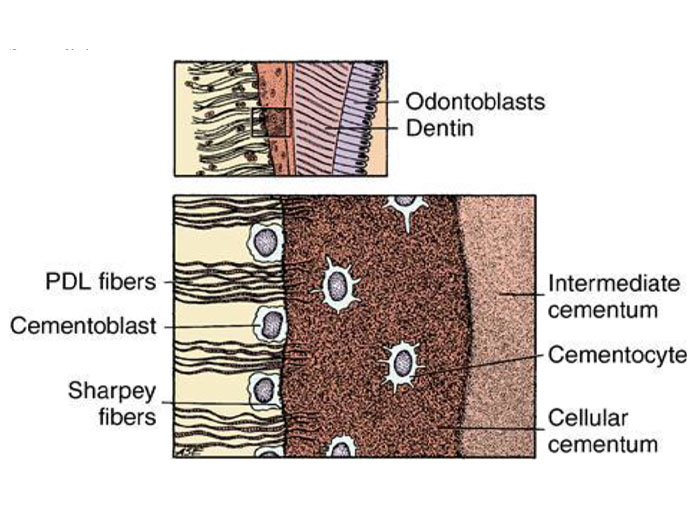
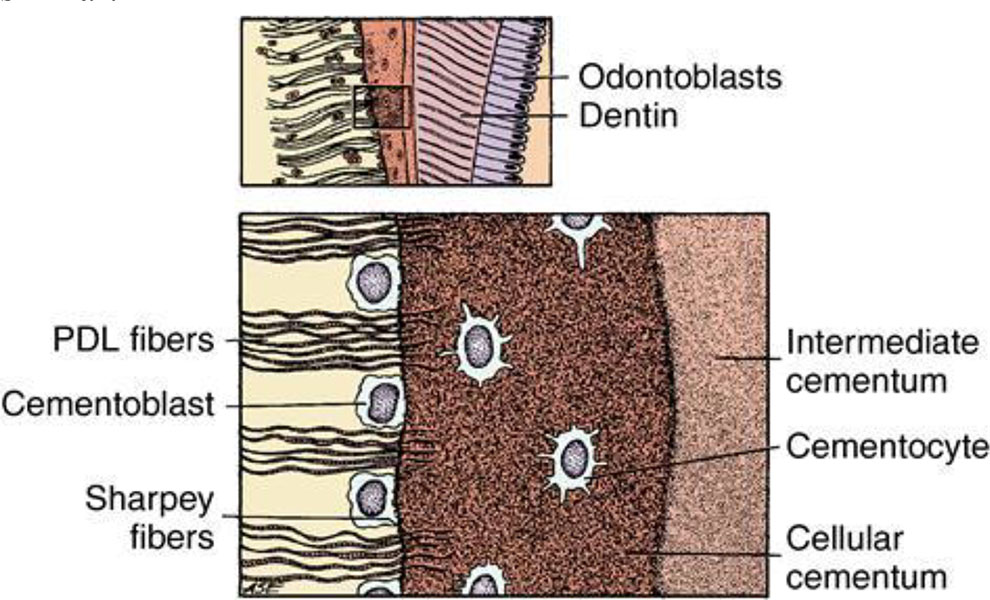
1. Intermediate cementum is
a) Between enamel and cementum
b) Found at dentinocemental junction
c) Apical third
d) Coronal third
ANSWER b
The intermediate cementum is a layer of calcified tissue between the dentin and the cementum at the periphery of dental roots. The mineralization pattern of the intermediate cementum and the innermost layer of aprismatic enamel in the crowns has been shown to be very similar.
2. Periodontal ligament has predominantly
a) Type II collagen fibers
b) Oxytalan fibers
c) Elastic fibers
d) Type I collagen fibers
ANSWER d
- Periodontal ligament (PDL) plays critical roles in the development and maintenance of periodontium such as tooth eruption and dissipation of masticatory force.
- The mechanical properties of PDL are mainly derived from fibrillar type I collagen, the most abundant extracellular component
- Type I collagen is thought to be produced by the odontoblasts as dentin, secreted by these cells, is composed of type I collagen
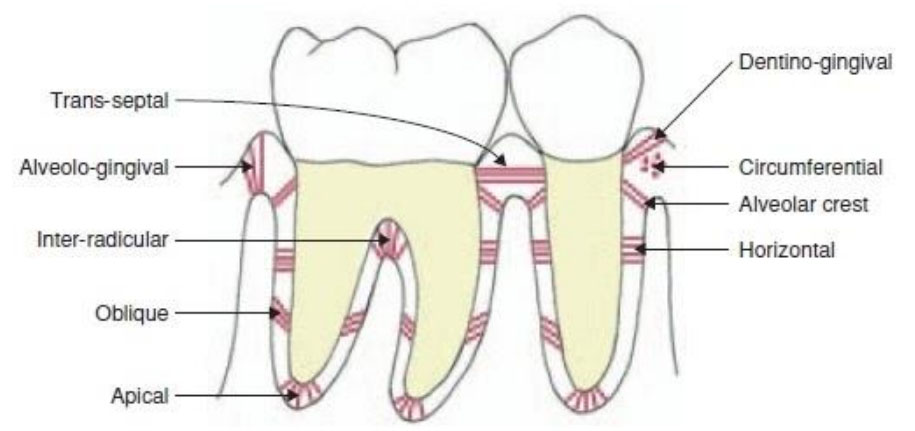
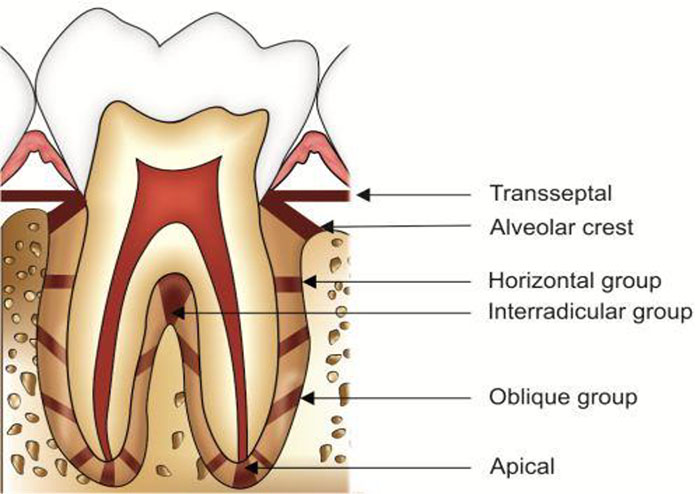
3. Group of fibers which resist masticatory force
a) Dento gingival
b) Transeptal
c) Oblique
d) Horizontal
ANSWER c
Oblique fibres are the most abundant fibre group in the PDL, extending from the cementum in a coronal direction obliquely to the alveolar bone. They resist vertical and intrusive forces, thus bear a large part of the vertical masticatory stresses and transfer them into tension on the alveolar bone
4. In deciduous teeth commonest type of cementoenamel junction seen is
a) Edge to edge
b) Overlap
c) Enamel and centum do not meet
d) All the above
ANSWER a
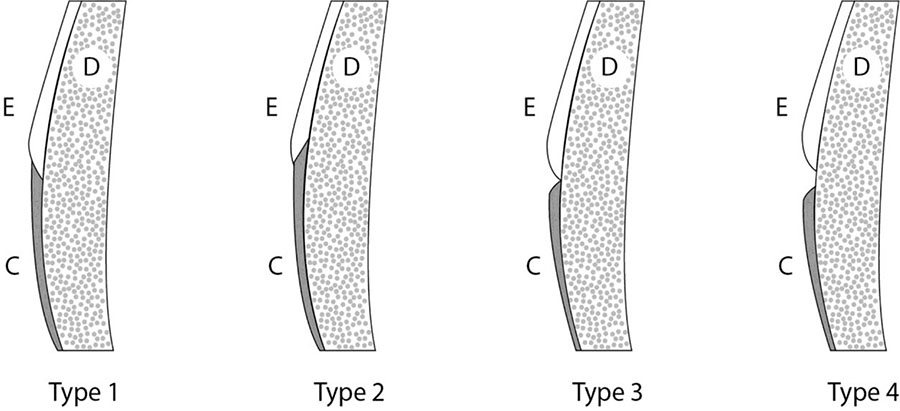
The cementoenamel junction (CEJ) can have different morphologies, known as Choquet cases or types
| TYPE 1 | The cementum overlaps the enamel |
| TYPE 2 | The enamel overlaps the cementum |
| TYPE 3 | The relationship between the cementum and enamel is edge-toedge |
| TYPE 4 | There is a gap between the enamel and the cementum, with exposed dentin |
5. Which of the following group of fibers are not attached to alveolar bone
a) Transseptal
b) Horizontal
c) Oblique
d) Apical
ANSWER a
- Transseptal fibers extend over the alveolar bone crest and are embedded in the cementum of adjacent teeth where they form an interdental ligament.
- These fibers work to keep the teeth aligned.
- These fibers may be considered as belonging to the gingival tissue as they do not have an osseous attachment.