- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]
CELLS OF PULP
The dental pulp is the part in the center of a tooth made up of living connective tissue
Cells found in the dental pulp include fibroblasts (the principal cell), odontoblasts, defence cells like histiocytes, macrophage, granulocytes, mast cells and plasma cells and Undifferentiated Cells
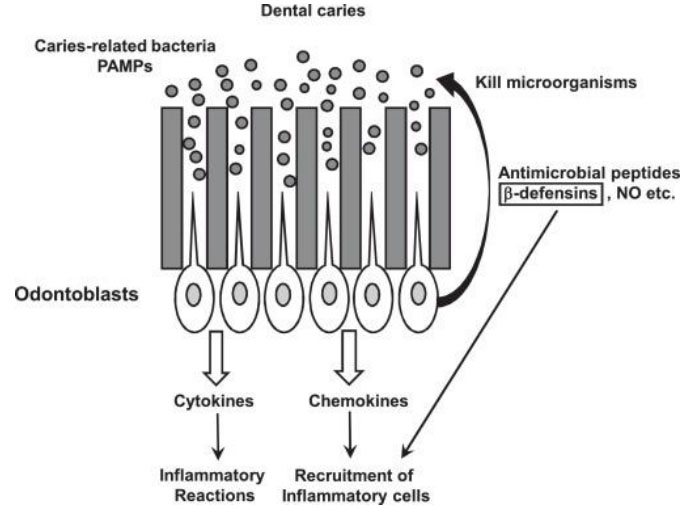
ODONTOBLASTS
- A Peripheral area of the pulp where the odontoblasts reside is termed odontogenic zone.
- Arranged in Palisading pattern cells are tall columnar forming a layer of 3 to 5 cells in depth.
- Shape may vary – Cornal pulp- columnar – Midportion - cuboidal – Apical region – Flattened
- These cells have large process extending into dentin
- The no of odontoblasts corresponds to the number of dentinal tubules Average no of odontoblasts estimated to 45,000 per Sq.mm of odontogenic zone.
- Odontoblasts in the crown are larger than in the root.
- Shape of the odontoblasts also reflect the functional activity of the cell.
- During active phase, cells show increase in endoplasmic reticulum golgi appartus and secretory vesicles.
- Resting (or) Non active phase cells are flattened little cytoplasm condensed chromatin and decrease no of ER
- Synthesis of non collagenous substances like sialoprotein, phosphophoryn, osteocalcin, ostenoectin & osteopontin
- Odontogenic process are those which Odontoblasts give off a single process that extends into dentin and housed within dentinal tubules
- These process devoid of major organelles
- They contain abundance of microtubular filaments and coated vesicles
- JUNCTIONAL COMPLEX are numerous junctions such as gap junctions tight junction and desmosomes are found between odontoblasts.
- Indicating exchange of ions and small molecules.
- They promote cell to cell adhension and play a role in maintaining polarity of odontoblasts

FIBROBLASTS
- The fibroblasts are the most abundant cells of dental pulp and they play pivotal roles in the normal physiologic function of the pulp.
- The fibroblasts are much more numerous in the coronal part of the pulp, where they form the cell-rich zone.
- The main function of these cells is to form and maintain the extracellular matrix of the dental pulp, which consists of collagen and ground substance.
- In young pulp the fibroblasts actively synthesize matrix and have the following morphological features: oval shape, pale stained nucleus with fine granular chromatin and a quite abundant cytoplasm.
- As demand synthesis decreases with age, the fibroblasts appear as flattened spindle shaped cells with reduced cytoplasm and a flattened nucleus with condensed chromatin.
- When they are properly stimulated, the fibroblasts of dental pulp have ability to ingest and also to damage collagen.
- Dental pulp cells, especially dental pulp fibroblasts, are known to synthesize various mediators of inflammation, such as IL-6 (6), IL-8, and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in response to caries-related bacterial components
UNDIFFERENTIATED ECTO-MESENCHYMAL CELLS
- Undifferentiated ecto-mesenchymal cells are the main source of the connective tissue of the dental pulp.
- These mesenchymal cells are distributed through out the pulp, frequently around the perivascular area - believed to be toti potent cell.
- Undifferentiated ectomesenchymal cells are found in the cell-rich zone and in the central zone of the dental pulp and are often related to blood vessels.
- By light microscopy, undifferentiated ecto-mesenchymal cells appear as large, star-shaped cells with a large nucleus, centrally located.
- These cells have an abundant cytoplasm and fine, branched cytoplasmic extensions.
- With age, the number of undifferentiated ecto-mesenchymal cells decreases, which limits the regenerative potential of the dental pulp
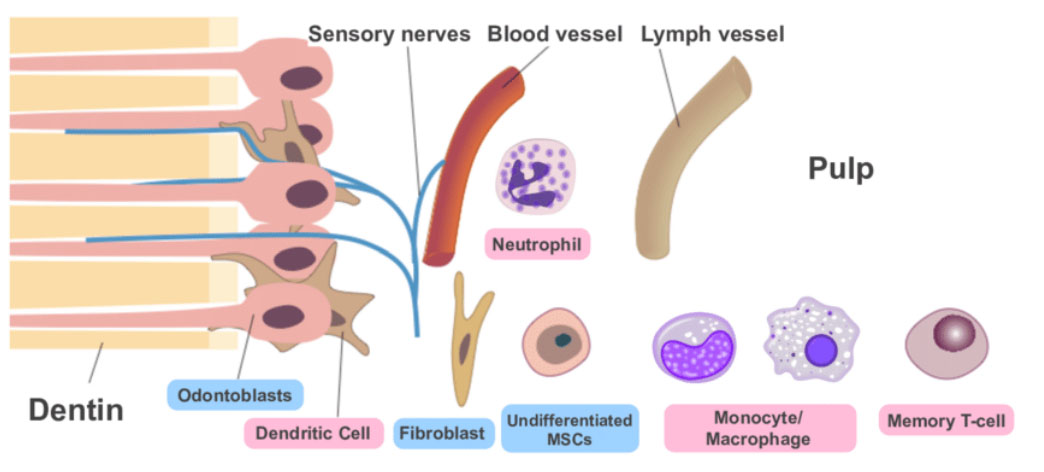
DEFENCE CELLS or IMMUNOCOMPETANT CELLS
- They play a major role local inflammation and immunity.
- They are recruited from blood stream and remain as transient inhabitants in pulp
- These cells are
| MACROPHAGE |
|
| MAST CELLS |
|
| LYMPHOCYTES |
|
| EOSINOPHILS |
|
Related posts
April 10, 2025


