- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]
What is ESR?
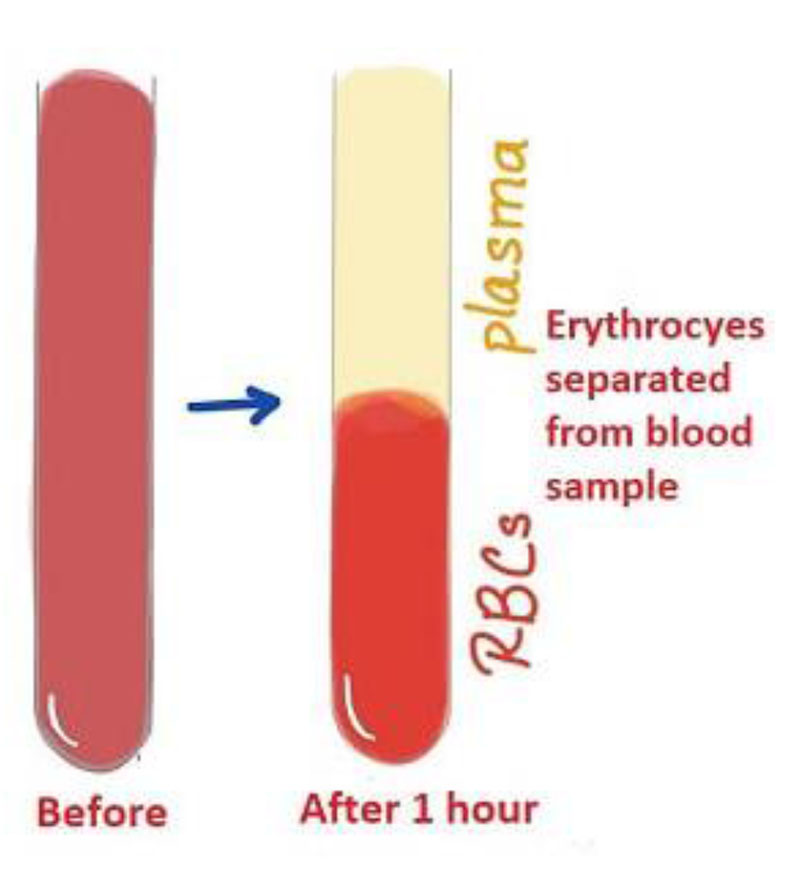
The erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) is the rate at which red blood cells in anticoagulated whole blood descend in a standardized tube over a period of one hour. It is a common hematology test.
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) is a nonspecific test for inflammation.
- It is easy to perform, widely available and inexpensive making it a widely used screening test
Why esr is done?
- The erythrocyte sedimentation rate (sedimentation rate, sed rate, and ESR for short) is a common hematology test that may indicate and monitor an increase in inflammatory activity within the body caused by one or more conditions such as autoimmune disease, infections or tumors.
- The ESR is not specific for any one disease but is used in combination with other tests to determine the presence of increased inflammatory activity.
- Known as a sickness indicator.
Principle
When the anti-coagulated blood is allowed to stand vertically, the red cells will settle towards the bottom of the tube till they form a packed column in a given interval of time. The process of sediment6ation is called ESR.
Mechanism
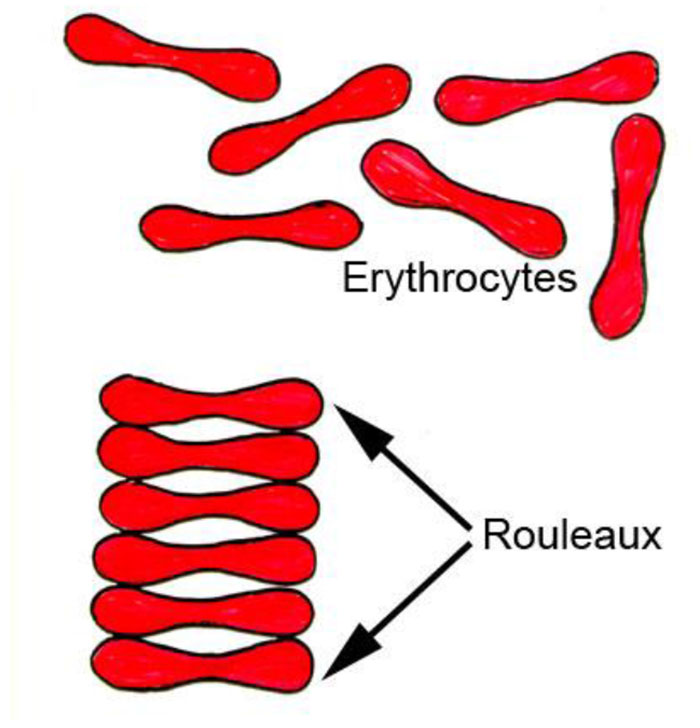
- Normal RBCs settle slowly as they do not form rouleaux. Instead, they gently repel each other due to the negative charge on their surfaces.
- The ESR is governed by the balance between pro-sedimentation factors, mainly fibrinogen, and those factors resisting sedimentation, namely the negative charge of the erythrocytes (zeta potential).
- When an inflammatory process is present, the high proportion of fibrinogen in the blood causes red blood cells to stick to each other.
- The red cells form stacks called rouleaux which settle faster, due to their increased density.
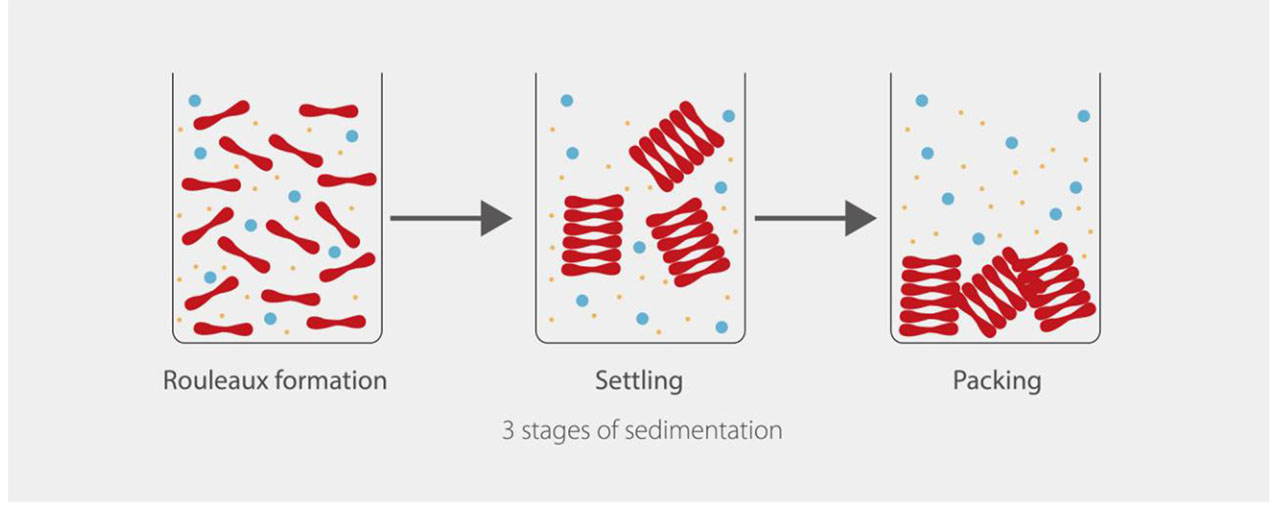
STAGES
There are three stages in erythrocyte sedimentation
- Rouleaux formation (10 minutes) Red cells stack together like pair of coins
- Sedimentation or settling stage (40 minutes)
- Packing stage - 10 minutes (sedimentation slows and cells start to pack at the bottom of the tube)
The ESR is affected by three factors:
- Erythrocytes
- Plasma Composition
- Mechanical/Technical Factors
Causes of elevation and reduction
| Elevated esr | Reduction in esr |
|---|---|
| Inflammation Fibrinogen, other clotting proteins, and alpha globulin are positively charged, thus increasing the ESR. |
An increased number of red blood cells (polycythemia) causes reduced ESR as blood viscosity increases |
| Non-inflammatory conditions Plasma albumin concentration, size, shape, and number of red blood cells, and the concentration of immunoglobulin can affect the ESR. Eg anemia,obesity etc |
A high ESR test result may be from a condition that causes inflammation, such as:
- Arteritis
- Arthritis
- Systemic vasculitis
- Polymyalgia rheumatica
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Kidney disease
- Infection
- Rheumatoid arthritis and other autoimmune diseases
- Heart disease
- Certain cancers
- It is also high in pregnancy
A low ESR test result means your red blood cells sank more slowly than normal. This may be caused by conditions such as:
- A blood disorder, such as:
- Polycythemia
- Sickle cell disease (SCD)
- Leukocytosis, a very high white blood cell count (WBC)
- Heart failure
- Certain kidney and liver problems
Values
Normal values for the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), as obtained using the Westergren method, are as follows
- Male <50 years old ≤15 mm/hr
- Female <50 years old ≤ 20 mm/hr
- Male >50 years old ≤20 mm/hr
- Female >50 years old ≤30 mm/hr
- Child ≤10 mm/hr
The ESR is typically higher in females than in males and increased gradually with age
Methods of estimation esr
| MANUAL | AUTOMATED |
|---|---|
|
|
Westergren method:
- The Westergren method requires collecting 2 ml of venous blood into a tube containing 0 .5 ml of sodium citrate.
- It should be stored no longer than 2 hours at room temperature or 6 hours at 4 °C.
- The blood is drawn into a Westergren-Katz tube to the 200 mm mark.
- The tube is placed in a rack in a strictly vertical position for 1 hour at room temperature, at which time the distance from the lowest point of the surface meniscus to the upper limit of the red cell sediment is measured.
- The distance of fall of erythrocytes, expressed as millimeters in 1 hour, is the ESR.

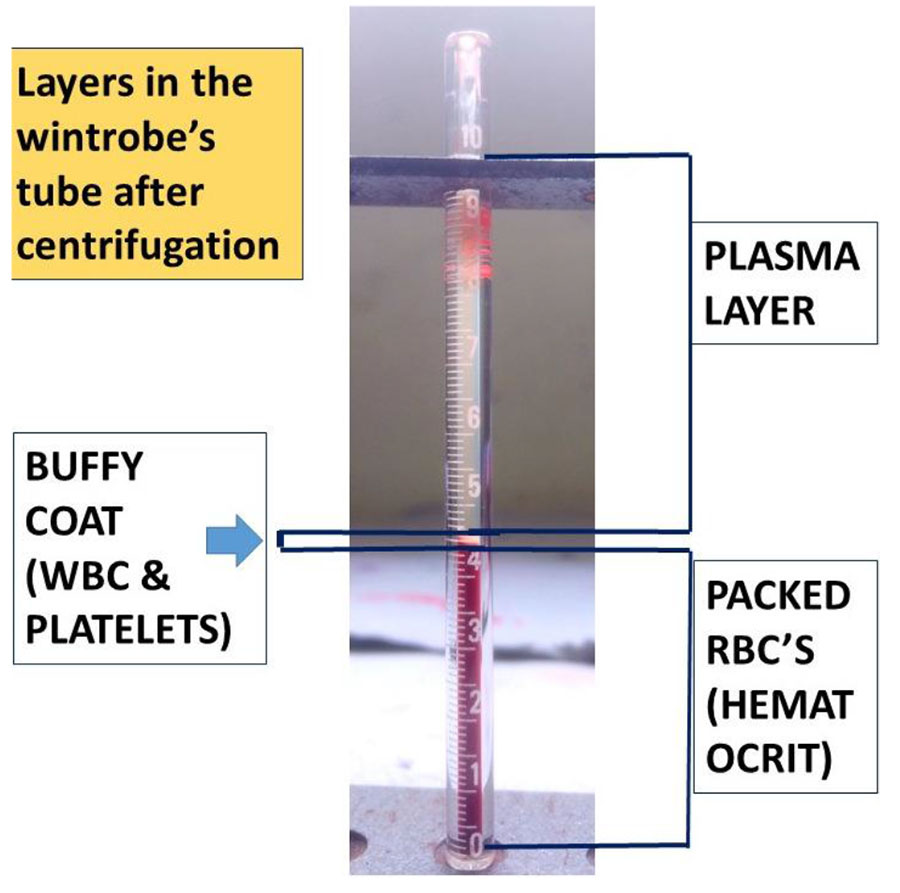
Wintrobe method:
- The Wintrobe method is performed similarly except that the Wintrobe tube is smaller in diameter than the Westergren tube and only 100 mm long.
- EDTA anticoagulated blood without extra diluent is drawn into the tube, and the rate of fall of red blood cells is measured in millimeters after 1 hour.
- The shorter column makes this method less sensitive than the Westergren method because the maximal possible abnormal value is lower.
- However, this method is more practical for demonstration purposes.
Zeta sedimentation rate (ZSR)
- It is not affected by anemia or globulin proteins.
- The normal range is the same for males and females. It uses a small amount of blood.
- This is good for children because of the small blood volume.
- It is calculated from the hematocrit and zitacrit and reported as a percentage.
Procedure for Zitacrit:
- A small-bore capillary tube is filled with blood from the finger prick.
- This capillary is spun in the special centrifuge called the Zetafuge (Coulter diagnostic).
- This tube is read on the special reader to get the value called zitacrit.
- Calculation as %: Zitacrit (% of sedimented RBCs)/hematocrit = Result expressed as % (percentage).
Automated Mini-Ves ESR:
- Automatic Mini-Ves ESR measures in 20 minutes instead of one hour.
- This 20-minute ESR reading correlates to the 1-hour Westergren method.
- 1mL of sample is drawn up into a 0.109 mol/L sodium citrate solution.
- It is placed in the Mini-VES machine.
- This instrument record the reading via its optical assembly.
- The second reading is recorded after 20 minutes to give the ESR value.