- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]

It originates in the seventh nerve nucleus in the brain stem (pons), enters the middle ear andmastoid and exits the skull at the stylomastoid foramen just in front of the mastoid process.From here it enters the parotid gland where it divides into its branches.
The facial nerve is associated with the derivatives of the second pharyngeal arch.
FIBERS:
- General somatic afferent (GSA)
- Special visceral afferent (SVA)
- General visceral efferent (GVE)
- Special visceral efferent (SVE, branchiomotor)
FUNCTIONS
Special visceral efferent (SVE) fibers
Special visceral efferent, or branchiomotor fibers in the facial nerve supply the flat skeletal muscles of the face and scalp, the stapedius muscle of the middle ear, the posterior belly of the digastric muscle, and the stylohyoid muscle. They belong to neurons whose cell bodies are located in the motor neuron of facial nerve.
General visceral efferent (GVE) fibers
General visceral efferent fibers in the facial nerve are involved in parasympathetic component of the autonomic nervous system and play an important role in the innervation of the lacrimal gland, nasal and palatine glands as well as the submandibular and sublingual glands. They belong to neurons whose cell bodies are located in the superior salivatory nucleus.
General somatic afferent (GSA) fibers
General somatic afferent (i.e. sensory) fibers belonging to neurons whose cell bodies which are located in the geniculate ganglion provide innervation of the skin around the external acoustic meatus and the retroauricular region. They synapse with second order neurons in the principal sensory nucleus of trigeminal nerve.
Special visceral afferent (GVA) fibers
The facial nerve (chorda tympani branch) has a special sensory function and is responsible for carrying special visceral afferent fibers to convey taste sensation from the anterior two thirds of the tongue and soft palate. They belong to neurons whose cells bodies are located in the geniculate ganglion, and synapse in the nucleus of solitary tract.
ASSOCIATED NUCLEI:
- Motor nucleus of facial nerve (SVE)
- Superior salivatory nucleus (GVE)
- Nucleus of solitary tract (SVA)
- Principal sensory nucleus of trigeminal nerve (GSA)
ASSOCIATED GANGLIA:
Geniculate ganglion (pterygopalatine ganglion, otic ganglion, submandibular ganglion)
EMBRYOLOGY
- During the third week of the embryo, the facioacoustic primordium develops, and this structure is what ultimately gives rise to the facial nerve.
- During the fourth week of life, the facial nerve splits into two: the chorda tympani and the caudal main trunk.
- At the beginning of the fifth week, the geniculate ganglion and the nervus intermedius develop.
- The facial muscles originate from the second branchial arch during the seventh and eighth weeks.
- The peripheral segment of the facial nerve undergoes extensive branching from week 10 to 15. Ossification of the bony canal takes place from the 16th week to birth.
ANATOMICAL COURSE
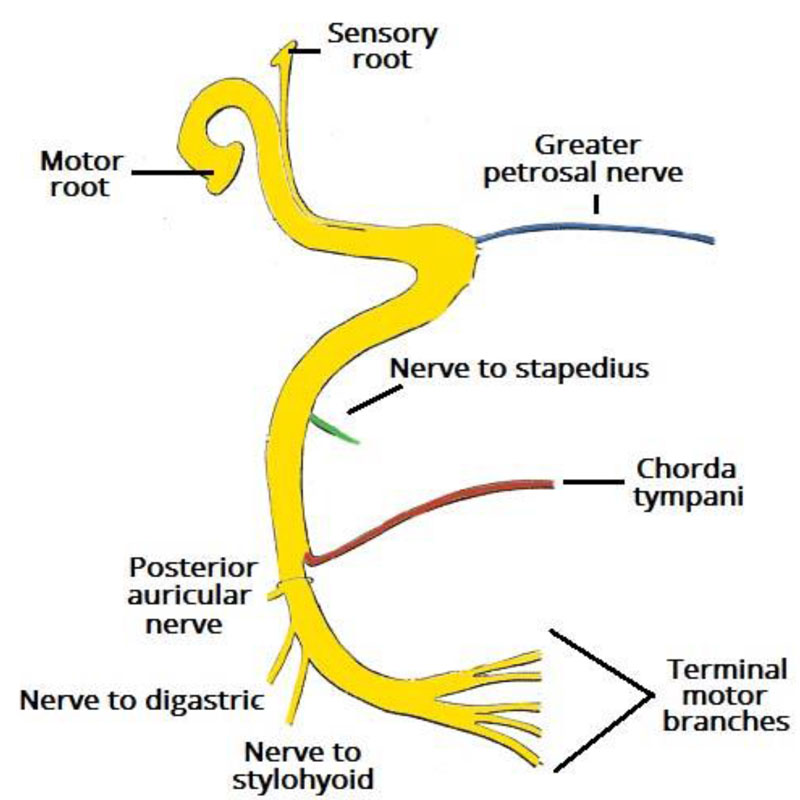
The facial nerve (CN VII) arises from two divisions: a motor root and a smaller sensory root, commonly referred to as the intermediate nerve.
- Intracranial – the course of the nerve through the cranial cavity, and the cranium itself.
- Extracranial – the course of the nerve outside the cranium, through the face and neck.
INTRACRANIAL
- The nerve arises in the pons, an area of the brainstem.
- It begins as two roots; a large motor root, and a small sensory root (the part of the facial nerve that arises from the sensory root is sometimes known as the intermediate nerve).
- The two roots travel through the internal acoustic meatus, a 1cm long opening in the petrous part of the temporal bone.
- Still within the temporal bone, the roots leave the internal acoustic meatus, and enter into the facial canal.
- The canal is a ‘Z’ shaped structure. Within the facial canal, three important events occur.
- The two roots fuse to form the facial nerve
- The nerve forms the geniculate ganglion (a ganglion is a collection of nerve cell bodies).
- And the nerve gives rise to:
- Greater petrosal nerve – parasympathetic fibres to mucous glands and lacrimal gland.
- Nerve to stapedius – motor fibres to stapedius muscle of the middle ear.
- Chorda tympani – special sensory fibres to the anterior 2/3 tongue and parasympathetic fibres to the submandibular and sublingual glands.
- The facial nerve then exits the facial canal (and the cranium) via the stylomastoid foramen.
- This is an exit located just posterior to the styloid process of the temporal bone.
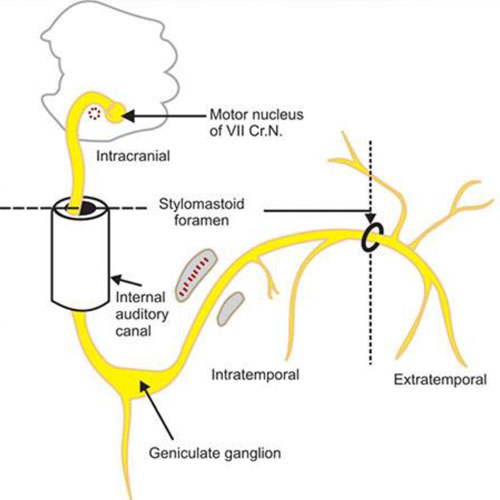
EXTRACRANIAL
- After exiting the skull, the facial nerve turns superiorly to run just anterior to the outer ear.
- The facial nerve leaves the facial canal through the stylomastoid foramen.
- It then gives off the posterior auricular nerve before continuing to enter the parotid gland located in the parotidomasseteric region of the face.
- It concludes its course by piercing the parotid gland, of which five terminal branches arise to form the parotid plexus
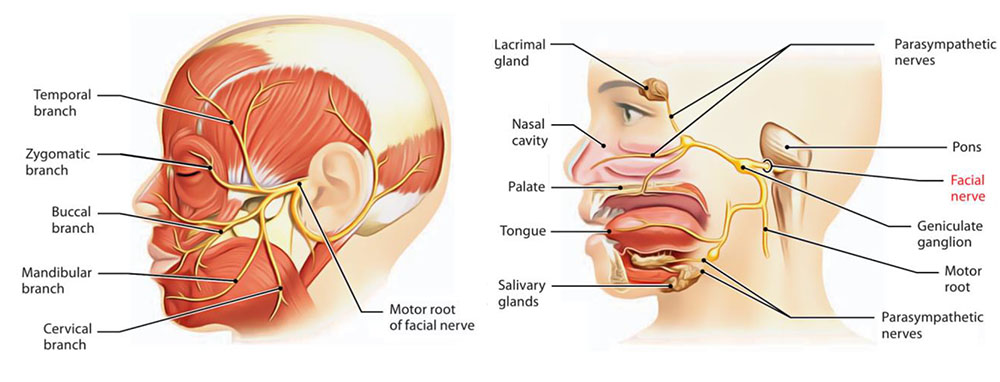
- Within the parotid gland, the nerve terminates by splitting into five branches:
- Temporal branch
- Zygomatic branch
- Buccal branch
- Marginal mandibular branch
- Cervical branch
BRANCHES
- WITHIN THE FACIAL CANAL :
- Greater petrosal neve
- The nerve to the stapedius
- The chorda tympani
- AT ITS EXIT FROM STYLOMASTOID FORAMEN
- Posterior auricular
- Diagastric
- Stylohyoid
- TERMINAL BRANCHES
- Temporal
- Zygomatic
- Buccal
- Marginal mandibular
- Cervical
- Communicating branches with adjacent cranial & spinal nerves.
IT SUPPLIES
- Motor – muscles of facial expression, posterior belly of the digastric, stylohyoid and stapedius muscles.
- Sensory – a small area around the concha of the external ear.
- Special Sensory – provides special taste sensation to the anterior 2/3 of the tongue via the chorda tympani
- Parasympathetic – supplies many of the glands of the head and neck, including:
- Submandibular and sublingual salivary glands.
- Nasal, palatine and pharyngeal mucous glands.
- Lacrimal glands.
MOTOR FUNCTIONS
- All these muscles are derivatives of the second pharyngeal arch.
- The first motor branch arises within the facial canal; the nerve to stapedius.
- Posterior auricular nerve – Ascends in front of the mastoid process, and innervates the intrinsic and extrinsic muscles of the outer ear. It also supplies the occipital part of the occipitofrontalis muscle.
- Nerve to the posterior belly of the digastric muscle – Innervates the posterior belly of the digastric muscle (a suprahyoid muscle of the neck). It is responsible for raising the hyoid bone.
- Nerve to the stylohyoid muscle – Innervates the stylohyoid muscle (a suprahyoid muscle of the neck). It is responsible for raising the hyoid bone.
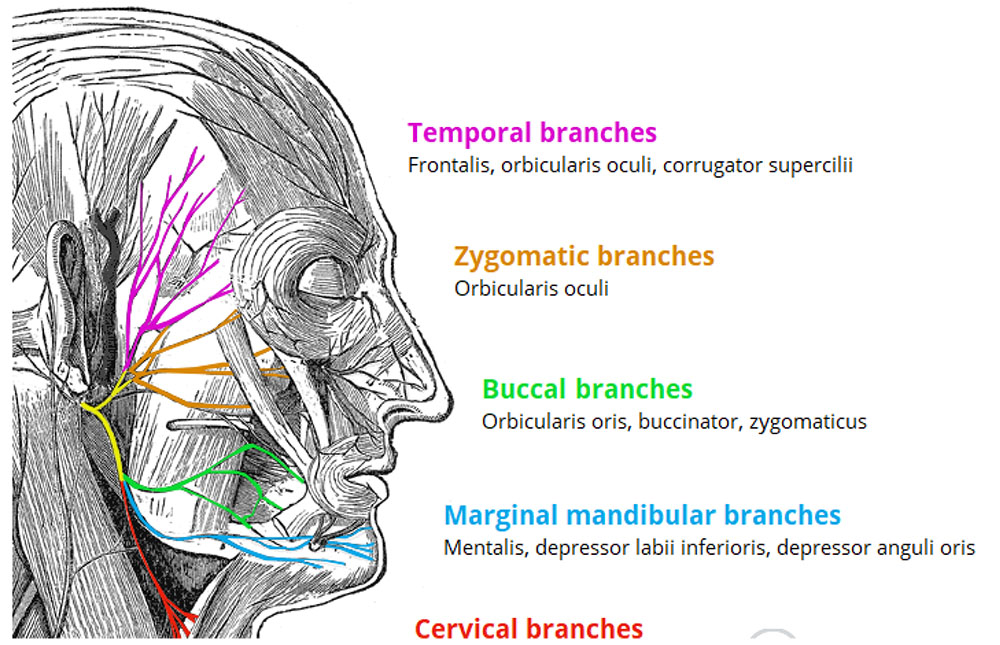
- Within the parotid gland, the facial nerve terminates by bifurcating into five motor branches. These innervate the muscles of facial expression:
- Temporal – Innervates the frontalis, orbicularis oculi and corrugator supercilii.
- Zygomatic – Innervates the orbicularis oculi.
- Buccal – Innervates the orbicularis oris, buccinator and zygomaticus.
- Marginal mandibular – Innervates the depressor labii inferioris, depressor anguli oris and mentalis.
- Cervical – Innervates the platysma.
SPECIAL SENSORY FUNCTIONS
- The chorda tympani branch of the facial nerve is responsible for innervating the anterior 2/3 of the tongue with the special sense of taste
- The nerve arises in the facial canal, and travels across the bones of the middle ear, exiting via the petrotympanic fissure, and entering the infratemporal fossa.
- Within the infratemporal fossa, the chorda tympani ‘hitchhikes’ upon the lingual nerve.
- The parasympathetic fibres of the chorda tympani stay with the lingual nerve, but the main body of the nerve leaves to innervate the anterior 2/3 of the tongue.
PARASYMPATHETIC FUNCTIONS
The parasympathetic fibres of the facial nerve are carried by the greater petrosal and chorda tympani branches.
APPLIED ANATOMY
- Bell’s palsy.
- Paralysis of facial nerve.
- Parotid gland pathology – e.g a tumour, parotitis, surgery.
- Infection of the nerve – particularly by the herpes virus.
- Compression during forceps delivery – the neonatal mastoid process is not fully developed and does not provide complete protection of the nerve.
- Idiopathic – If no definitive cause can be found then the disease is termed Bell’s palsy.


