- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]
DEFINICTION
Killey and kay(1966) – cyst constitutes an epithelium –lined sac filled with fluid or semifluid material
Killey and kay (1966) – revised definition”A cyst is an abnormal cavity in hard or soft tissue which is contains fluid, semifluid or gas and is often encapsulated and lined by epithelium.”
Kramer’s(1974) – A cyst is pathologic cavity having fluid, semifluid, or gaseous contents that are not created by the accumulation of pus; frequently, but not always, is lined by epithelium.
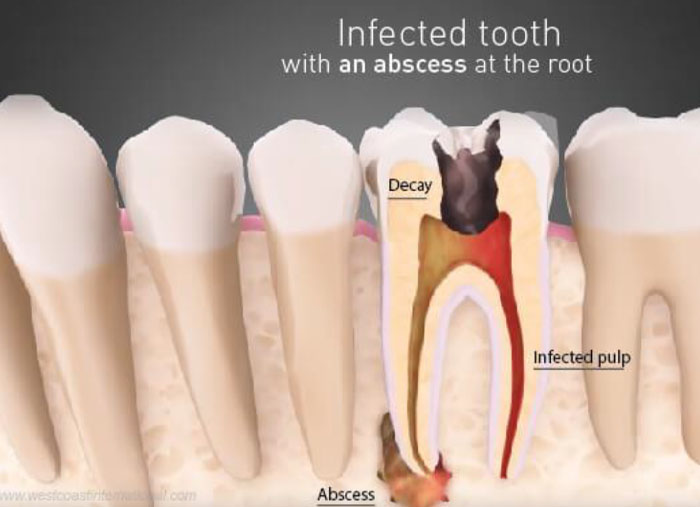
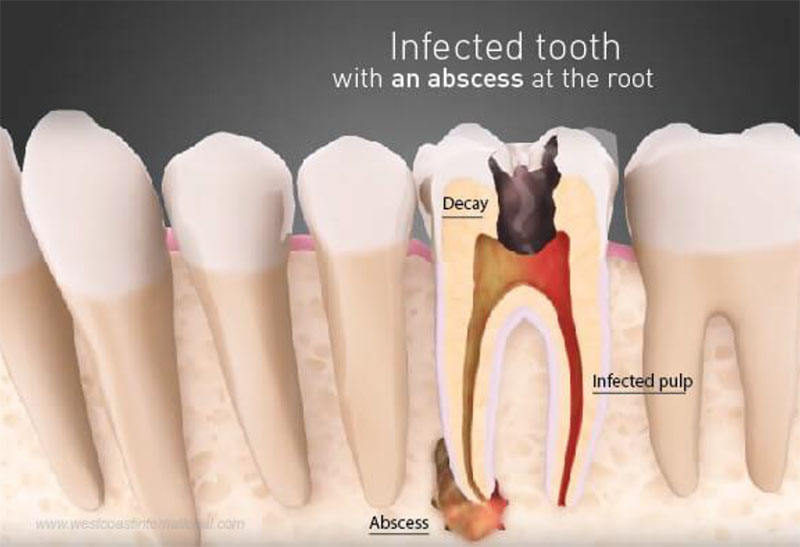
PARTS OF CYST:
- There are three main parts of cyst:
- Wall that is made of connective tissue
- Epithelial lining
- Lumen of the cyst.
CAUSES OF CYST:
Common causes of cyst includes
- Tumors
- Genetic conditions
- Infections
- A fault in an organ of a developing embryo.
- A defect in the cells.
- Chronic inflammatory conditions.
- Blockages of ducts in the body that causes a fluid build up.
- Impact injury that breaks a vessel.
TYPES:
- True cyst: These are the cysts that are lined by epithelium e.g Dentigerous cyst, Radicular cyst.
- Pseudo cyst : These are the cysts that are not lined by epithelium. E.g Solitary bone cyst,Aneurismal bone cyst
CLASSIFICATION
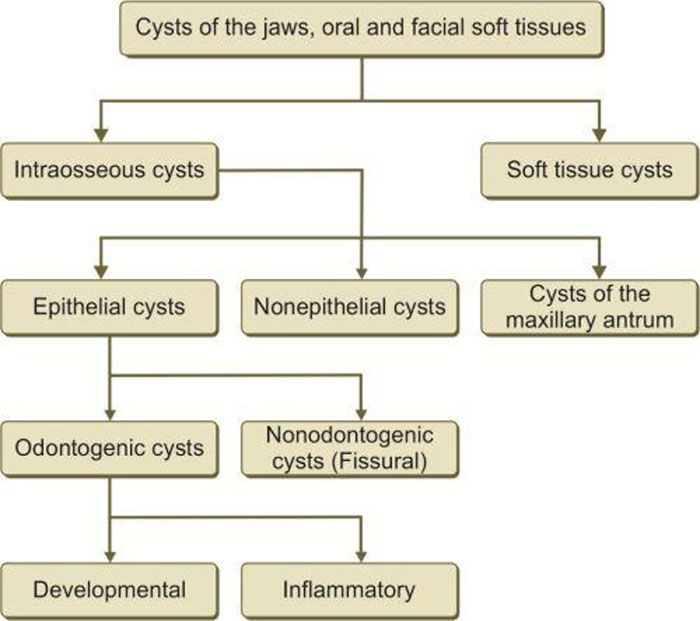
Various classifications have been given:
- WHO Classification
- Shears Classification
- Shafers Classification
WHO Classification is divided into 2 Types:
- Developmental
- Inflammatory
Developmental:
I. Odontogenic:
- Primordial ( Kerato ) cyst.
- Gingival cyst.
- Eruption cyst.
- Dentigerous ( Follicular ) cyst.
II. Non Odontogenic:
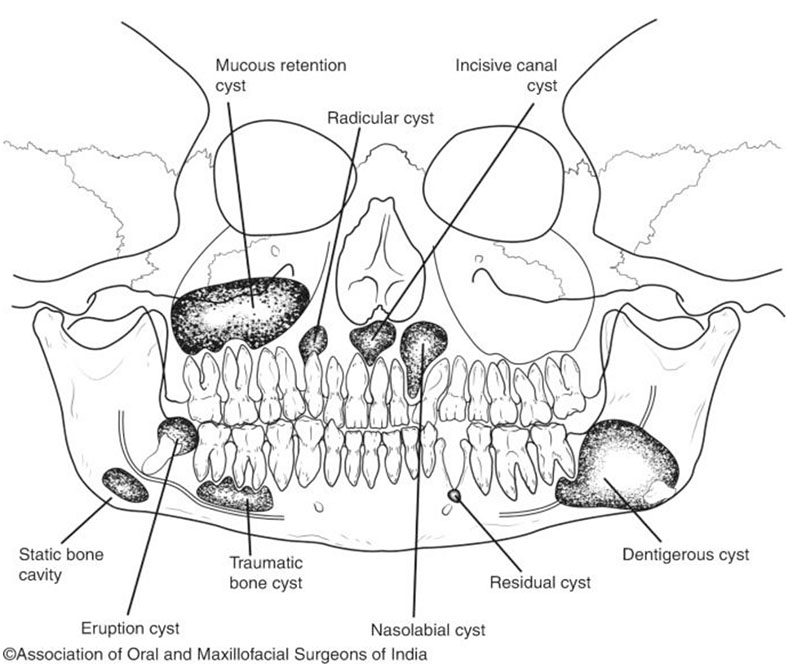
- Naso palatine duct ( Incisive canal ) cyst.
- Globulomaxillary cyst.
- Naso labial ( naso alveolar ) cyst.
SHEAR’S CLASSIFICATION
It is divided into 3 types:
- Cysts of Jaw
- Cysts associated with Maxillary Antrum
- Cysts of the soft tissues of the Face, Neck and Mouth Cysts Of Jaw:
Epithelial Cysts Of Jaws:
I. Odontogenic:
A).Developmental
- Primordial (Kerato) cyst .
- Gingival cyst of infants .
- Gingival cyst of adults .
- Lateral periodontal cyst .
- Dentigerous cyst .
- Eruption cyst .
- Calcifying odontogenic cyst.
B). Inflammatory
- Radicular cyst .
- Residual cyst .
- Inflammatory collateral cyst.
- Para dental cyst.
II. Non-Odontogenic:
- Nasopalatine duct cyst & Incisive canal cyst
- Median palatine cyst
- Median alveolar cyst
- Median mandibular cyst
- Globulomaxillary cyst
- Naso labial (naso alveolar) cyst
Non Epithelial Cysts:
A). Simple bone cyst:
- Traumatic
- Solitary
- Hemorrhagic
B). Aneurysmal bone cyst.
Cysts Associated with the Maxillary Antrum
- Benign mucosal cyst .
- Surgical ciliated cyst of maxilla.
Cysts of the Soft tissues of the Face, Neck and Mouth
- Dermoid & Epidermoid cysts
- Branchial cleft cyst (Lympho epithelial cyst)
- Thyroglossal duct cyst
- Anterior median lingual cyst
- Oral cyst with gastro intestinal epithelium
- Cystic hygroma
- Cysts of the salivary glands
- Parasitic cysts: Hydatid cyst, Cysticerous cellulosae
SHAFERS CLASSIFICATION
- Primordial cyst .
- Dentigerous cyst & Eruption cyst .
- Periodontal cyst :
a. Apical periodontal cyst .
b. Lateral periodontal cyst . - Gingival cyst :
a. Gingival cyst of newborn(Dental lamina cyst)
b. Gingival cyst of adult . - Odontogenic kerato cyst .(Jaw cyst, Basal cell nevus & Bifid rib syndrome)
- Calcifying odontogenic cyst .
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF CYST
• Phases of cyst development :
CYST INITIATION
Stimulation of cell rests of Malassez in response to INFLAMMATION elicited by - baterial infection of pulp - direct response to necrotic pulp tissue.
CYST FORMATION
- Proliferation of Epithelial Lining and fibrous Capsule
- Insufficient diffusion of oxygen and nutrients
- Death of central cells or disquamation of the central cells.
- Formation of a small cystic cavity
CYST ENLARGEMENT
- Attraction of fluid into tthe cyst cavity
- Retention of the fluid within the cavity
- Production of raised internal hydrostatic pressure
- Resorption of the surrounding bone with an increase in the size of the cavity
CLINICAL FEATURES
- Commonly seen in 1st and 3rd decade of life
- Males more affected than females
- Capable to becoming aggressive lesion
- Asymptomatic unless they develop into very large cyst or get infected
- Expansion of bone Facial asymmetry
- Displacement and root resorption of adjacent teeth
- Pain may occur if secondary infection supervenes
TREATMENT
- Marsuplization
- Enucleation of cyst together with removal of unerupted teeth
- This permits decompression of a resulting decrease in the size of bone defects.


