- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]
Tongue
Introduction
Tongue is one among the five sensory organ. It is the muscular organ situated in the floor of the mouth. It comprises of skeletal muscle which is voluntary in function.
Parts
- Root
- Tip (Apex)
- Body
ROOT
- It is the attached part of the tongue.
- It is attached to the Mandible and Hyoid bone by muscles.
- Nerve and blood vessels of the tongue enter through its root.
TIP (APEX)
- It is the anterior free end.
- It comes into contact with central incisors.
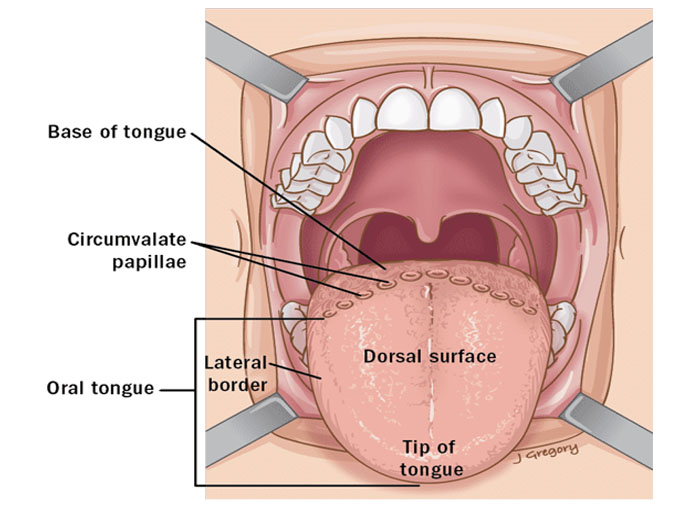
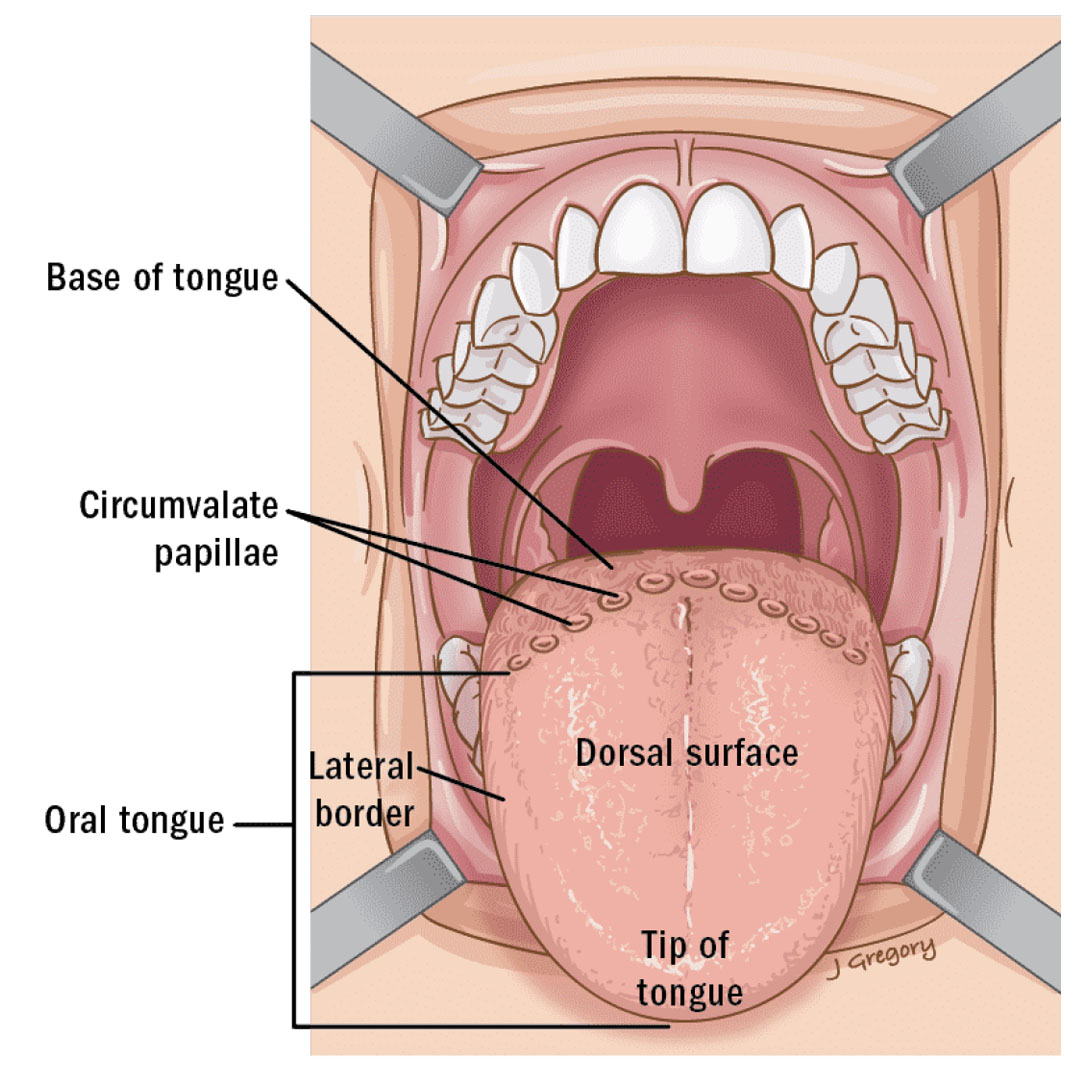
BODY
- The part of tongue, between its root and tip.
- It has two surfaces: DORSAL AND VENTRAL.
- It has two borders: Right lateral andLeft lateral.
Functions
- Deglutition
- Taste sensation
- Speech production
- Breast feeding
- Self-cleansing system
- Mastication
General Features Surfaces
- Two surfaces
- Superior surface
- Inferior surface
- Superior surface is divided into three parts
- Anterior 2/3 part called as Oral part
- Posterior 1/3 part called as Pharyngeal part
- Base(root) of tongue
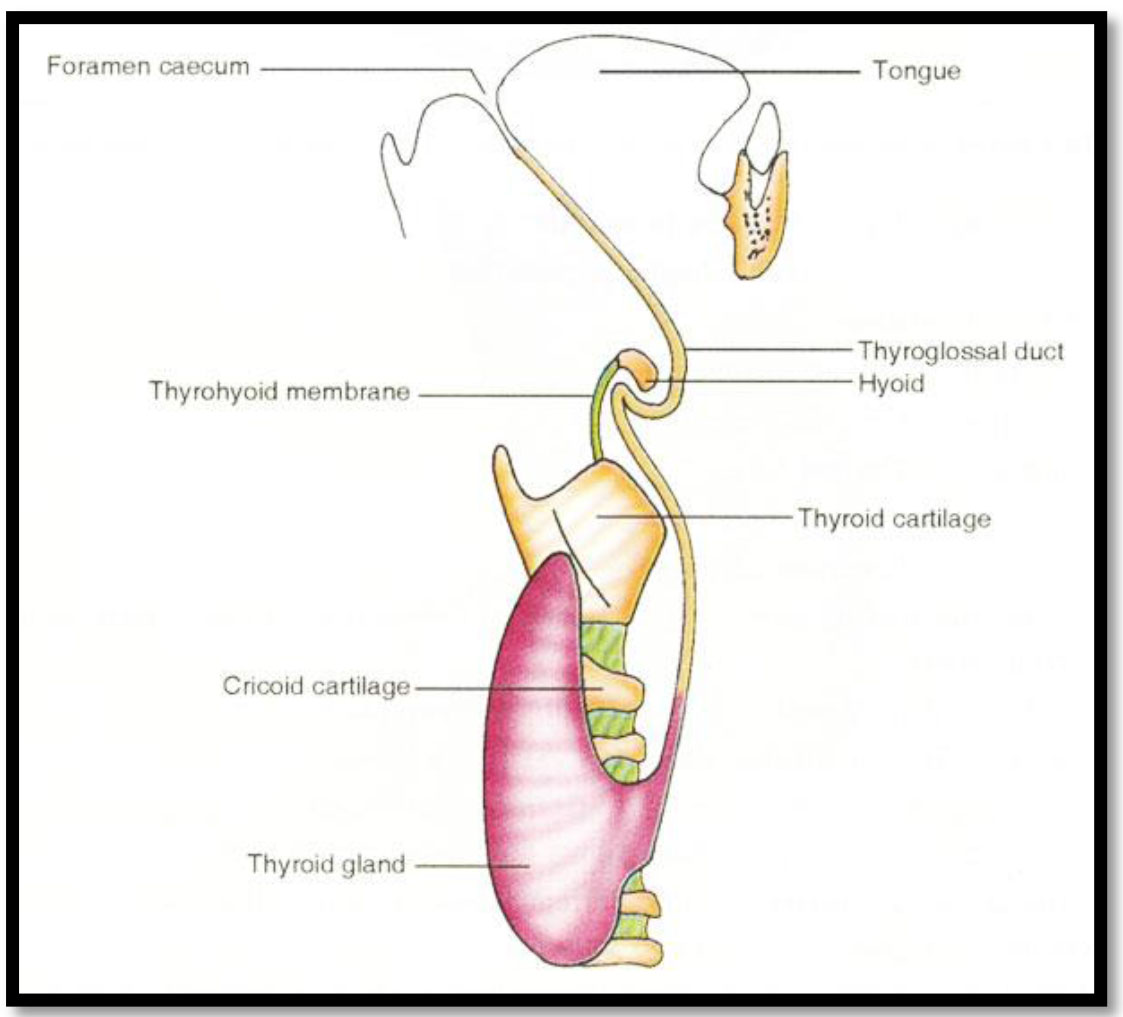
- TERMINAL SULCUS V-shaped sulcus divides tongue into anterior & posterior parts - Apex of sulcus marked by a pit - FORAMEN CECUM.
- Foramen cecum ,an embryological remnant, marks the upper end of thyroglossal duct.
- Sometime a thyroglossal duct persists and connects the foramen cecum with the thyroid gland in neck(thyroglossal cyst).
- Taste Buds - Four taste sensations, recently a fifth basic taste has been added: sour, sweet, salty, bitter and the recently added umami UMAMI.
- Base of tongue is far back and is bottom of tongue.
- Contributes to the front wall of pharynx.
- Movement can affect the diameter of pharynx i.e
- When it push forwards, thereby expanding the pharynx
- When it pull backwards, thereby constricting the pharynx
- Lacks papillae
- Inferior surface covered by smooth mucous membrane.
- In the midline , a mucosal fold called Frenulum connects the tongue with the floor of the mouth.
- Lateral to frenulum, deep lingual vein can be seen through the mucosa.
- Lateral to the lingual vein , mucosal fold called as plica fimbriata is present.
Pappilae
Indentation of any structure in the overlying epithelium is called papillae
Types of of papillae;
- Vallate/circumvallate
- Filiform
- Fungiform
- Foliate
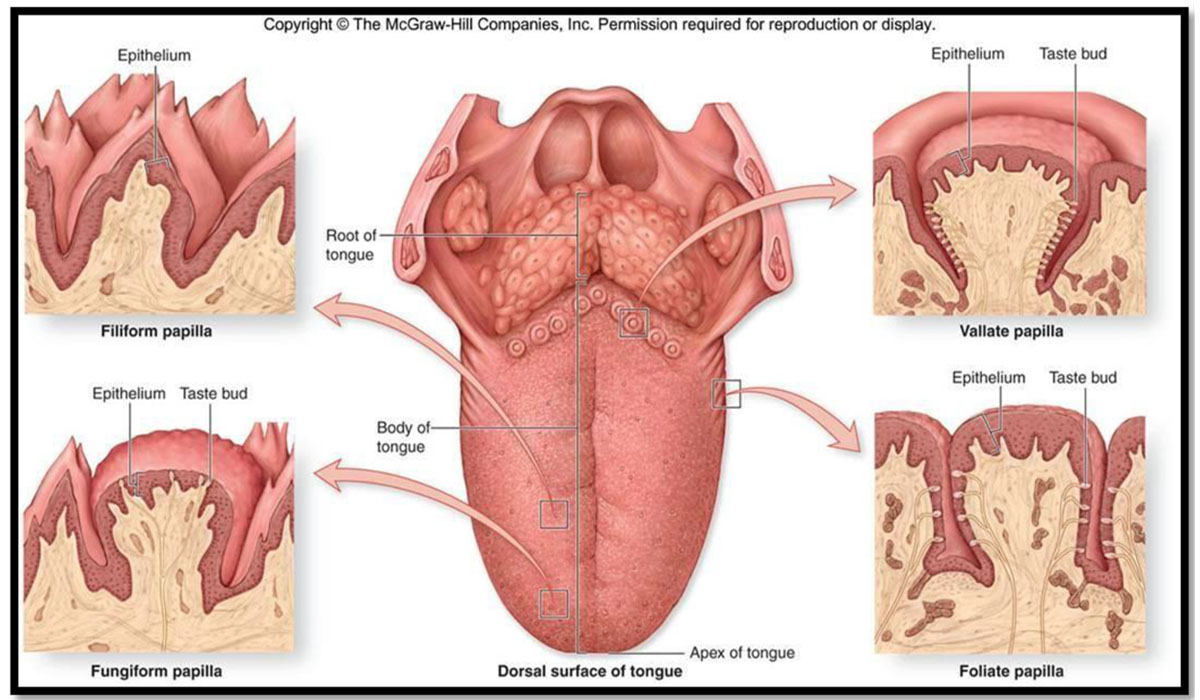
1. Vallate Papillae
- Largest (1-2 mm in diameter).
- Location- In front of sulcus terminalis in a ‘V’shaped row.
- Shape- Truncated cone.
- Each papilla is surrounded by a circular sulcus.
- Circular sulcus is bounded on its periphery by a wall (vallum).
- Ducts of several salivary glands open in the circular sulcus.
- Taste buds are present in the papilla and its vallum.
2. Filiform Papillae
- SHAPE: Thin, long papillae having pointed ends.
- Only papillae having no taste buds.
- NUMBER: numerous.
- These papillae are mechanical and not involved in gustation.
- Identified by increased keratinization.
- LOCATION: Present at pre-sulcal area of the tongue.
3. Fungiform Pappilae
- SHAPE: slightly mushroom-shaped if looked at in longitudinal section.
- Taste buds on their surfaces.
- LOCATION: apex of the tongue as well as the margins.
- Larger than filiform papillae.
4. Foliate Pappilae
- SHAPE: Short vertical folds.
- LOCATION: Present lateral to terminal sulcus and at margins.
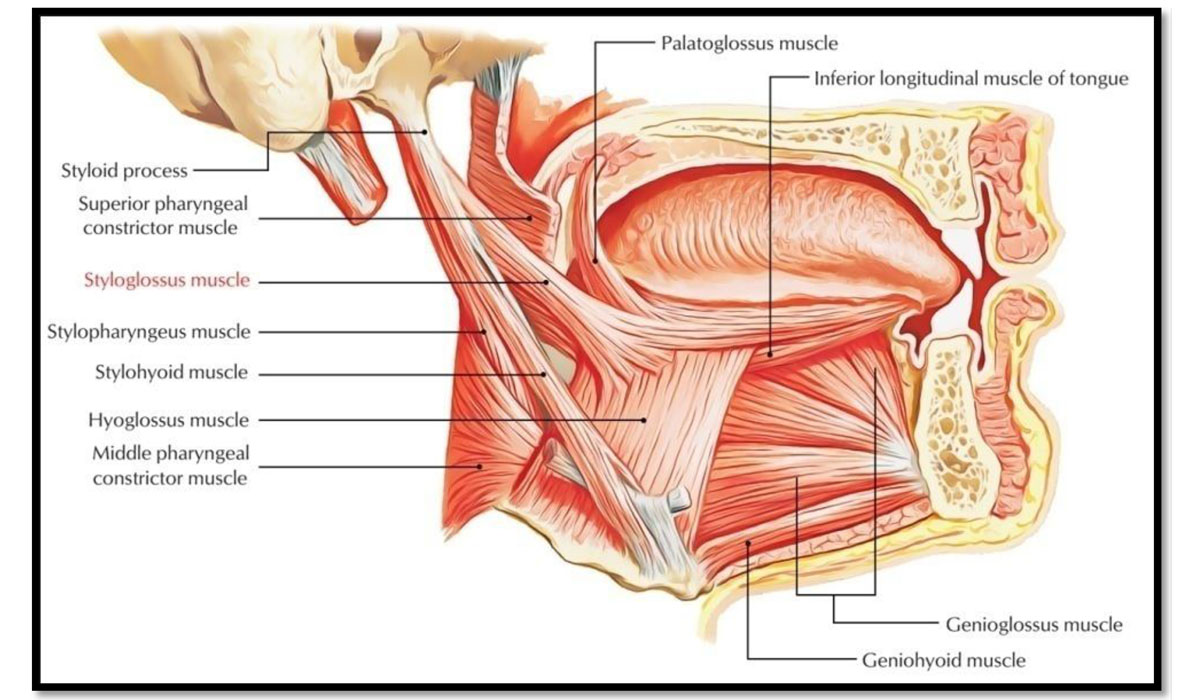
Muscles
All the muscles of the tongue are paired structures, with each copy being found on either side of the median fibrous septum.
2 types
- EXTRINSIC
- INTRINSIC
Intrinsic Muscles
The intrinsic muscles originate and attach to other structures within the tongue.
There are four paired intrinsic muscles of the tongue and they are named by the direction in which they travel.
- Superior longitudinal
- Inferior longitudinal
- Transverse
- Vertical muscles of the tongue
Extrinsic Muscles
The extrinsic muscles of the tongue originate from structures outside the tongue and insert onto it.
| ATTACHMENT | FUNCTION | |
|---|---|---|
| Genioglossus The genioglossus muscle is a large, thick muscle, which contributes significantly to the shape of the tongue. |
Arises from the mandibular symphysis. It inserts onto the body of the hyoid bone and the entire length of the tongue | Protrusion (‘sticking the tongue out’) and depression of the tongue. |
| Styloglossus The styloglossus is a thin, paired muscle, located on either side of the oropharynx. |
Originates from the styloid process of the temporal bone and inserts onto the lateral aspect of the tongue. | Depression and retraction of the tongue |
| Styloglossus The styloglossus is a thin, paired muscle, located on either side of the oropharynx. |
Originates from the styloid process of the temporal bone and inserts onto the lateral aspect of the tongue. | Reraction of tongue |
| Palatoglossus The palatoglossus muscle is also associated with the soft palate |
Arises from the palatine aponeurosis and inserts broadly along the tongue | Elevation of posterior tongue |
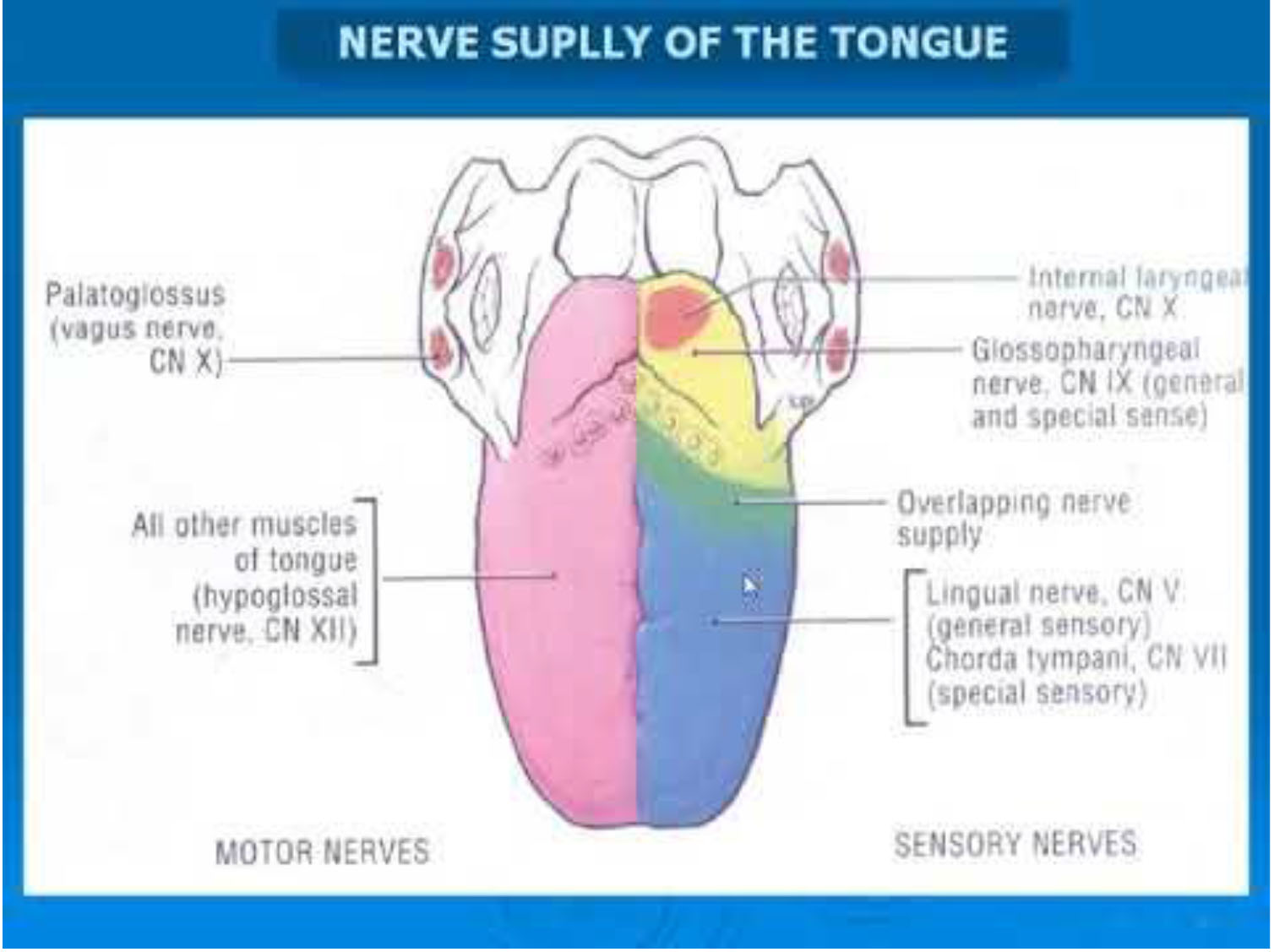
Nerve Supply
- In the anterior 2/3, general sensation is supplied by the trigeminal nerve (CNV).
- Specifically the lingual nerve, a branch of the mandibular nerve (CN V3).
- On the other hand, taste in the anterior 2/3 supplied from the facial nerve (CNVII). In the petrous part of the temporal bone, the facial nerve gives off three branches, one of which is chorda tympani. This travels through the middle ear, and continues on to the tongue.
- The posterior 1/3 of the tongue is slightly easier. Both touch and taste are supplied by the glossopharyngeal nerve (CNIX).
Blood Supply
- Lingual artery (branch of the external carotid) does most of the supply, but there is a branch from the facial artery, called the tonsillar artery, which can provide some collateral circulation.
- Drainage is by the lingual vein.
Lymphatic Drainage
- Anterior two thirds – initially into the submental and submandibular nodes, which empty into the deep cervical lymph nodes.
- Posterior third – directly into the deep cervical lymph nodes.
Related posts
April 10, 2025


