- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]
Leukemia
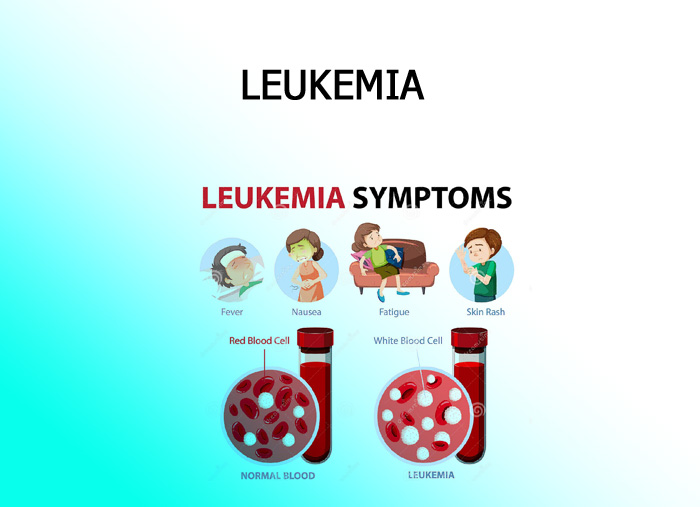
Leukemia is mainly of 4 types:
Acute myeloblastic leukemia (AML)
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL)
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML)
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)
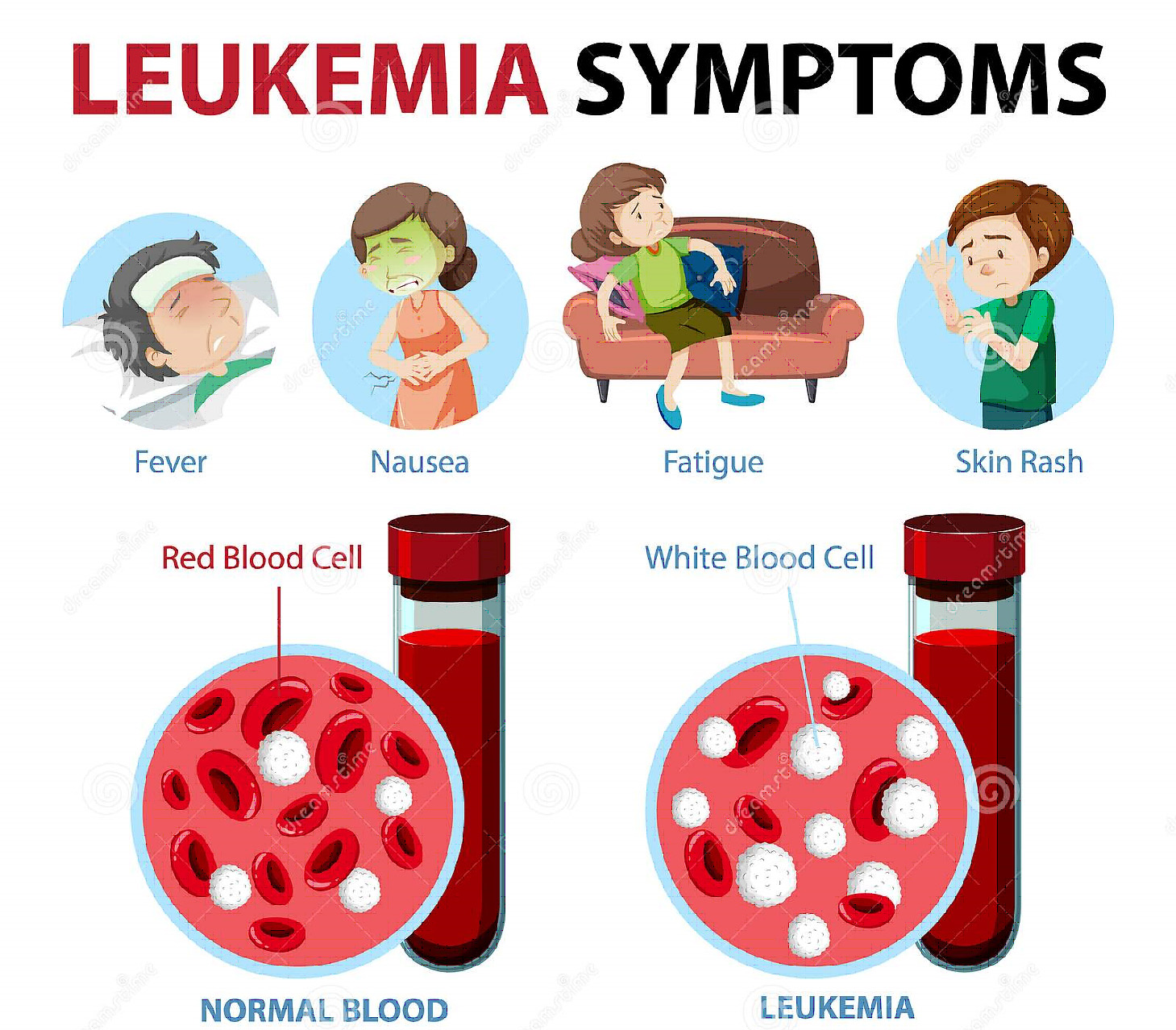
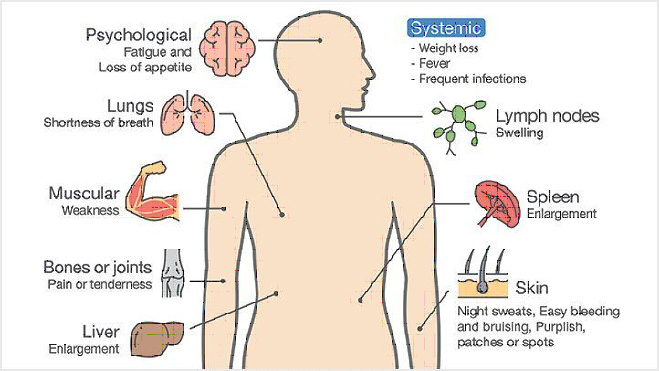
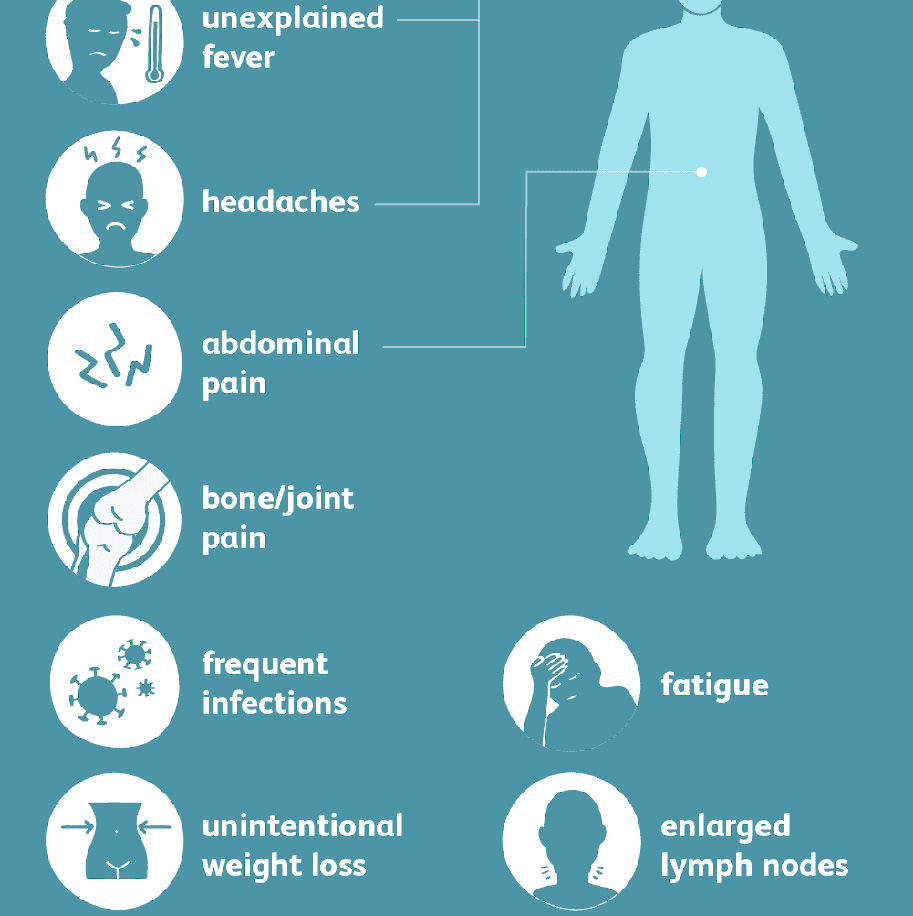
| Type | Important features |
| AML |
|
| ALL |
|
| CLL |
|
| CML |
|
Related posts
April 10, 2025
April 9, 2025
April 4, 2025




