- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]
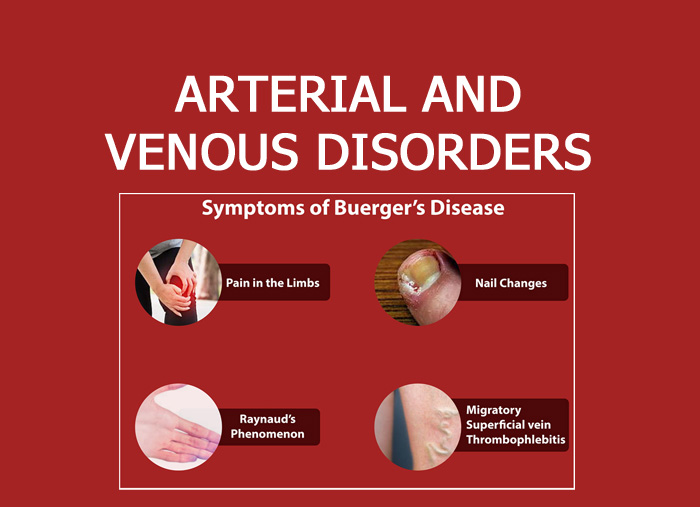
| BUERGER’S DISEASE | RAYNAUD’S SYNDROME |
| Arterial occlusive disease mainly affecting lower limbs | Vasospastic condition affecting upper limbs |
| Occurs in men from 20-40years and in smokers | Usually occurs in young women |
| Characterised by gangrene of the toes and fingers and corrugation of femoral arteries | Characterised by blanching of digits when exposed to cold and turning to red when the attack passes off |
| Abstinence from smoking and sympathectomy are useful in treating this disease. | Protection from cold and of calcium antagonists use is the conservative treatment. |


Intermittent claudication is a cramp like pain felt mostly in the calf muscle that;
- Is brought on by walking
- Is not present on taking the first step
- Is relieved by standing still
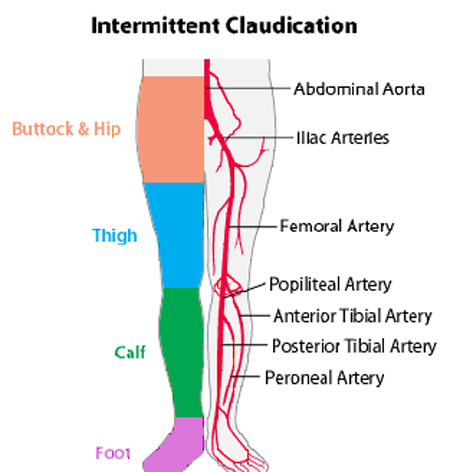
| Intermittent claudication | Rest pain |
| Cramp like pain felt mostly in the calf muscle | Severe pain felt in the foot at rest |
| It is brought on by walking and is relieved by standing still. It is not present on taking the fast step. | It made worse by lying down or elevation of foot and relieved by hanging the foot out of bed. |
Deep vein thrombosis is a serious life threatening condition characterised by the development of postthrombotic limb and venous ulceration. The frequent location is the lower limb and the commenest complication is pulmonary embolism. The signs and symptoms are swelling, pain, dilated superficial veins, calf tenderness and redness.
Risk factors for deep vein thrombosis are:
- Old age
- Recent orthopaedic surgery of lower limbs
- Oral contraceptives
- Thrombophilia
- Nephrotic syndrome

Virchows predisposing factors for deep vein thrombosis are:
- Changes in vessel wall
- Decreased blood flow
- Increased coagulability of the blood
Varicose veins occur commonly due to incompetence of the valves of long and short saphenous veins resulting in reverse flow and dilation of the vein below the valve. Varicose veins occasionally may develop complications like superficial thrombophlebitis, haemorrhage or venous ulceration. The main surgical treatment are to ligate the source of venous reflex and to remove the incompetent saphenous trunks.

- Duplex ultrasound scanning is the recent investigation for varicose veins. Tests for locating the incompetent valves communicating the superficial land deep veins in varicose veins are:
Trendelenberg test
Tourniquet test
Perthes test
Schwartz test
Pratt’s test
Morissey’s cough impulse test
Fegans method to indicate the sites of perforations
Management of varicose veins:
A) Compression hosiery:
Relies on graduated external pressure to improve deep venous return
B) Ultrasound guided foam sclerotherapy:
- Involves injection of detergent directly into the superficial veins.
- The detergent destroys the lipid membrane of endothelial cells causing them to shed, leading to thrombosis, fibrosis and obliteration.
C) Endovenous laser ablation:
Involves insertion of a laser fibre into the lumen of an incompetent vein, with subsequent thermal ablation of the vein.
Click here to view QA and Description for Arterial and Venous Disorders