- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]
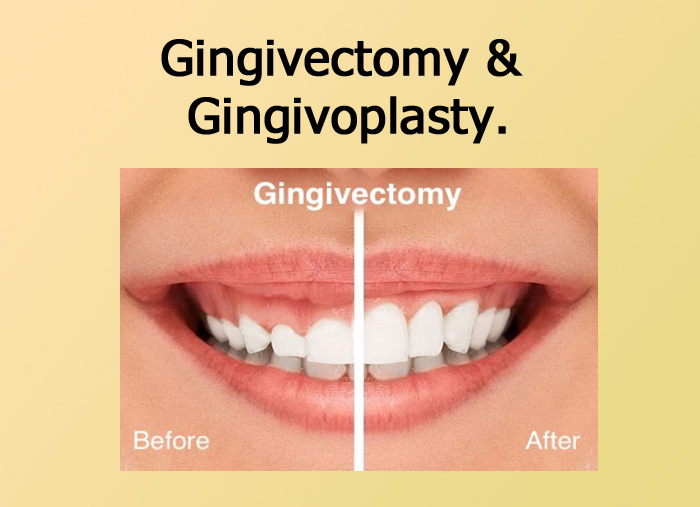
Gingivectomy
Excision of gingiva by removing the deceased pocket wall thereby exposing tooth surface which provides the visibility and access ability that are essential for the complete removal of irritating surface deposits and thorough smoothening of the roots.

Gingivoplasty.
It is the reshaping of the gingiva to create physiologic gingival contours with the sole purpose of recontouring the gingiva in the absence of pockets
Indications Of gingivectomy
- Supra Bony pocket
- Supra Bony periodontal Abscess
- Fibrous enlargement (pseudo pocket)
- Crown lengthening
- Aesthetic
Contraindications
- Fragile gingiva
- Bone Defect cannot be corrected
- Location of the base of the pocket epical to the mucogingival junction
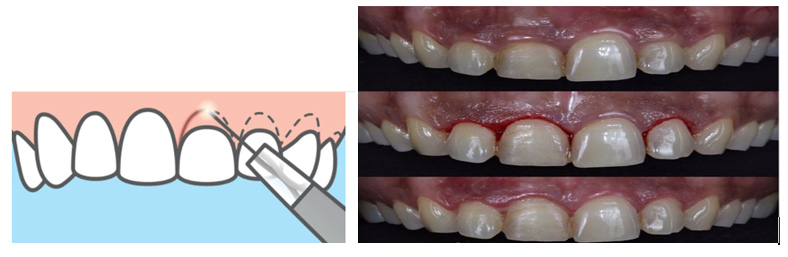
Types of gingivectomy
1. Surgical gingivectomy
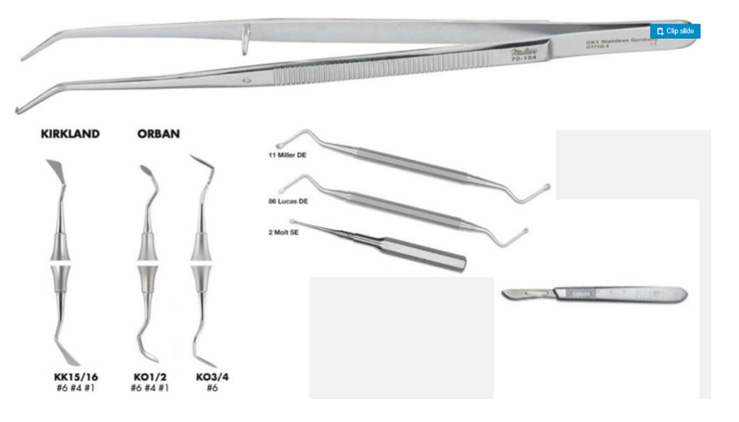
Instruments required
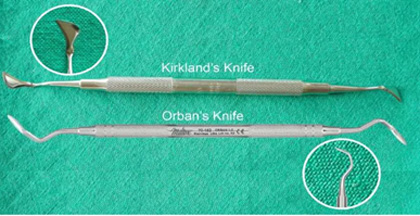
- Pocket markers: Crane-Kaplan pocket marker/ Goldman-fox pocket marker.
- Broad-bladed, round scalpels: Goldman fox No. 7/ Kirk-land knife.
- Interproximal knife: Goldman fox No.8,9 & 10 & orban’s knife
- Surgical handles: Bard parker handle no 3 & angulated handle ( blade no 11,12 &15)
- Tissue nippers.
2. Gingivectomy by chemosurgery
Agent used 25 % phenol with 75% camphor,5% paraformaldehyde in ZnO eugenol pack.
Advantages of chemo surgery
- No anaesthesia required for the procedure
- Procedure is easy to perform and require less instruments
Disadvantage
- Bone necrosis might result
- Periodontal Abscess might result
- Delayed would healing
- Subsequent plaque retention
- Bone resorption
3. Gingivectomy by electro surgery
Advantage
- Less bleeding
Disadvantages
- Necrosis of adjacent tissue and born resorption due to the production of heat during the procedure
4. Gingivectomy by cryosurgery
-52 – 60 degrees Celsius temperature is applied to the gingiva by means of a probe
Advantage
- Procedure does not cause pain and bleeding
5. Gingivectomy by laser
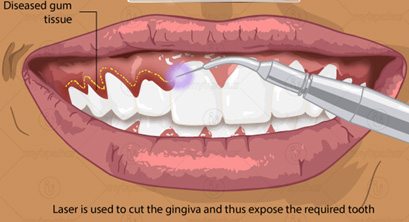
Types of laser used: Co2 laser & Nd: YAG laser
Advantages
- Least necrosis
- No post-operative dressing is required
Gingingivoplasty
Indications
- Correcting the grossly thickened gingival margin
- Correction of deformities like craters, clefts, gingival enlargements
- Varying levels of gingival margins.
Instruments used
Periodontal knife, scalpel, rotary coarse diamond electrodes

MCQ
1. Indications of gingivectomy
a) Edema of gingiva
b) Infrabony pockets
c) Adequate attached gingiva
d) Pocket depth below mucogingival level
Answer: C
Click here to view QA and Description for Gingivectomy & Gingivoplasty