- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]

A. 90mR
B. 120mR
C. 250mR
D. 300mR
Ans. A
Mean exposure of pantamograph is less than mean exposure of radiation from single dental IOPA xray which is 217mR. With improved techniques skin exposures from dental xray can be reduced as low as 1-10mR.
2. The maximum permissible dose of radiation to the operator of an xray machine is
A. 0.05 rem per year
B. 0.5 rem per year
C. 5.0 rem per year
D. 50 rem per year
Ans. C
3. The principal hazard to operator and patient is produced by what type of radiation
A. Gamma
B. Primary
C. Secondary
D. None of the above
Ans. C
4. Radiation produced from tube other than focal spot is called
A. Stray radiation
B. Scattered radiation
C. Characteristic radiation
D. Primary radiation
Ans. A
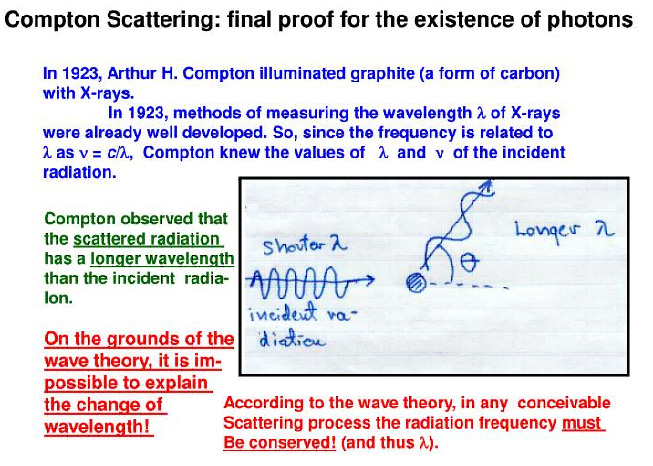
5. Major source of secondary scatteted radiation
A. Compton effect
B. Photoelectric effect
C. Thompson effect
D. All of the above
Ans. A
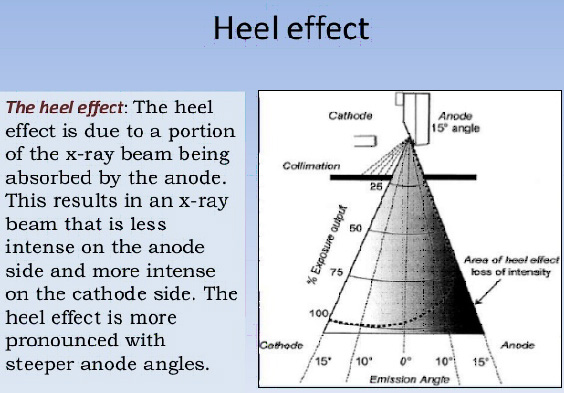
6. According to heel effect when cathode rays strike anode target, xray released with high intensity are found towards
A. Anode
B. Cathode
C. In between anode and cathode
D. None of the above
Ans. B
7. …………… is not a property of x rays
A. Ionisation
B. Action on photographic film
C. Excitation
D. Collimation
Ans. D
8. Commonly used collimating device
A. Aluminium filter
B. Lead diaphragm
C. Molybdenum cup
D. Tungsten filament
Ans. B

9. The xray collimators commonly used in dentistry include the following except
A. Diaphragm collimator
B. Tubular collimator
C. Rectangular collimator
D. Square collimator
Ans. D
Rectangular, round and tubular collimators are commonly used in dentistry.
The dental x ray beam should be collimated to a circle of 7cm in diameter.
10. Greatest decrease in overall radiation risk from dental xray to patients is achieved by
A. Using speed E film
B. Rectangular collimation
C. Using a lead apron
D. Increasing target film distance
Ans. B




