- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]
Pleomorphic Adenoma
- Benign epithelial tumor arising in salivary gland.
- Earlier it arises from epithelial and connective tissue. Therefore mixed tumour but later it is confirmed that it arises from epithelial tissue due to its morphological complicity.
- Site -upper lip, posterior and lateral aspect of palate, posterior part of hard palate.
- Female 40 to 50 years
Clinical features
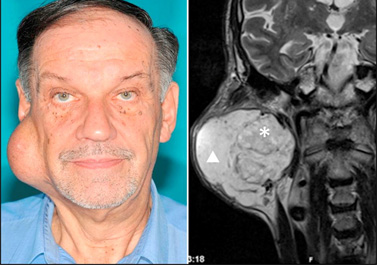
- slow growing, painless fluctuant movable swelling With no bleeding
- It produces lots of mucin.
- Single growth, multi nodular , For consistency
Differential diagnosis
- Mumps
- HeerFord syndrome (sarcoidosis)
- Parotitis
- SJogren syndrome
- TB lymphadenopathy
Investigation
FNAC
Biopsy
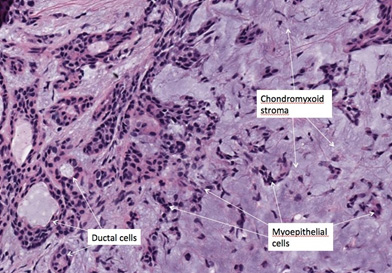
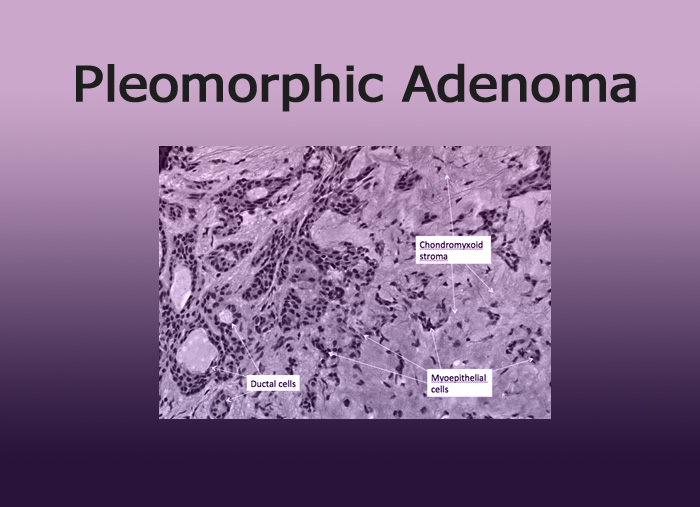
Histopathology
- Ductal pattern with mucin
- Islands( nests, sheets and cords)
- Squamous metaplasia
- Myoepithelial cells
- Osseous
- Adipocytes
- Myxoid
- Plasmacytoid
- Chondroid
- Fibrous
Treatment
Surgical excision
Radiation therapy is Contra indicated
Carcinoma Ex pleomorphic adenoma
- Malignant pleomorphic adenoma
- It constitutes 99 % of all cases of malignant mixer tumour.
- It develops in 6%of all isomorphic adenomas.
Etiology
- unknown etiology
- Exposure to radiation is thought to be a factor
- Malignant change may result from the development of accumulation Of genetic instability within tumor.
Clinical features
- Major salivary gland> Minor salivary gland
- Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma àmost frequently seen in parotid gland and the submandibular gland is less frequently involved.
- It originates deeper part of the parotid gland
- In minor salivary gland, palate is the most common.
- Slow growing, painless mass
- Painless usually present with symptoms and signs suggesting malignancy
Histopathology
- Malignant appearing cells are present adjacent to a typical appearing pleomorphic adenoma.
- Pleomorphic tumour cells with focally vacuolated cytoplasm.
- Mitotic figures are commonly seen Hindi nucleus.
- The malignant portion of the tumour can take the form of any epithelial malignancy like undifferentiated carcinoma or adenocarcinoma.
Treatment
Excision along with neck dissection.
Post operative radiotherapy.
MCQs
- Most common tumour of parotid gland is
- Pleomorphic adenoma
- ACC
- Cylindroma
- Epidermoid carcinoma
Answer: A
Pleomorphic adenoma is most common salivary gland tumor (60% cases) and most common parotid gland (85% cases).
Click here to view QA and Description for Pleomorphic Adenoma
Related posts
April 10, 2025
April 9, 2025
April 4, 2025




