- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]
1. In absence of oxygen, pyruvate is converted into lactate in muscle because
a) Lactate is the substrate from the downstream pathway
b) Lactate acts as a substrate for the formation of amino acid
c) during the product of lactate two ATP are produced
d) during lactate formation, NADH is reconverted into NAD.
Ans:D
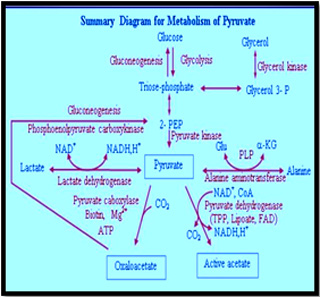
2. During prolong starvation, which of the following hormone is responsible for increasing gluconeogenesis in the liver
a) Insulin
b) Glucagon
c) TSH
d) Thyroxine
Ans: B
Gluconeogenesis occurs in the liver and kidneys. Gluconeogenesis supplies the needs for plasma glucose between meals. Gluconeogenesis is stimulated by the diabetogenic hormones (glucagon, growth hormone, epinephrine, and cortisol). Gluconeogenic substrates include glycerol, lactate, propionate, and certain amino acids. PEP carboxykinase catalyzes the rate-limiting reaction in gluconeogenesis. The dicarboxylic acid shuttle moves hydrocarbons from pyruvate to PEP in gluconeogenesis.
3. Gluconeogenesis is the production of glucose from non-carbohydrate molecules. Which of the following is not substrate for gluconeogenesis?
a) Lactate
b) Alanine
c) Glycerol
d) Acetyl CoA
Ans: D
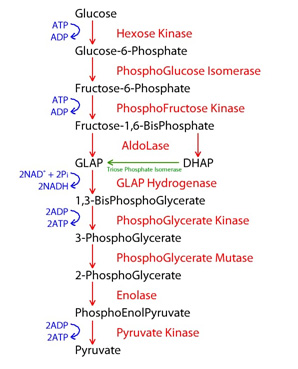
4. During the conversion of glucose to pyruvate, two NADH molecules are generated. Which of the following steps generates NADH?
a) Conversion of fructose-6-phosphate to fructose-1-6-bisphosphate
b) Conversion of glyceraldehydes-3-phosphate to 1-3-bisphosphoglycerate
c)Conversion of 3-phosphoglycerate to 2-phosphoglycerate
d) Conversion of phosphoenolpyruvate to pyruvate
Ans: B
The first phase of glycolysis requires energy, while the second phase completes the conversion to pyruvate and produces ATP and NADH for the cell to use for energy. Overall, the process of glycolysis produces a net gain of two pyruvate molecules, two ATP molecules, and two NADH molecules for the cell to use for energy.
5. Which of the following statement is true?
a) Glycolysis occurs only in mammalian cells
b) Glycolysis occurs in mitochondria
c) Glycolysis occurs in the presence and absence of oxygen
d) Glycolysis occurs when ATP concentration is high.
Ans: C
- Glycolysis: Oxidation of glucose to pyruvate in presence of O2 or lactate in absence of O2.
- Site: cytosol of all cells.
- Steps:
- Phase I (Energy utilization phase): Glucose is cleaved to two molecules of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate. This phase consumes 2 molecules of ATP.
- Phase II (Energy recovery phase): The two molecules of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate are converted to pyruvate under aerobic state with generation of 10 ATPs. Or lactate under anaerobic state with generation of 4 ATPs.
- All reactions are reversible except GK, PFK, PK.
6. Which of the following hormone decreases blood glucose and increases the uptake of glucose in various tissues like skeletal muscle, adipose tissues?
a) Glucagon
b) Epinephrine
c) Cortisol
d) Insulin
Ans:D
Insulin helps control postprandial glucose in three ways. Initially, insulin signals the cells of insulin-sensitive peripheral tissues, primarily skeletal muscle, to increase their uptake of glucose. Secondly, insulin acts on the liver to promote glycogenesis.
7. Which of the following glucose transporter (GLUT) are important in insulin-dependent glucose uptake?
a) GLUT1
b) GLUT2
c) GLUT3
d) GLUT4
Ans: D
GLUTS I, II and III are insulin-independent whereas GLUT IV is insulin-dependent glucose transporter. GLUT4 is an insulin-regulated glucose transporter which is responsible for insulin-regulated glucose uptake into fat and muscle cells.
8. In muscles, the pyruvate is converted into lactate. Find the correct statement
a) During lactate formation, NADH is reconverted into NAD
b) During the product of lactate two ATP are produced
c) Lactate is the substrate from the downstream pathway
d) Lactate acts as the substrate for the formation of amino acid
Ans: A
9. What is the net gain of ATP during the conversion of glucose to pyruvate?
a) 2 ATP
b) 4 ATP
c) 6 ATP
d) 1 ATP +1 GTP
Ans: A
10. Which of the following enzymes are not involved in galactose metabolism?
a) Galactokinase
b) Glucokinase
c) Galactose-1-Phosphate Uridyltransferase
d) UDP-Galactose 4- epimerase
Ans: B