- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]
Vitamins
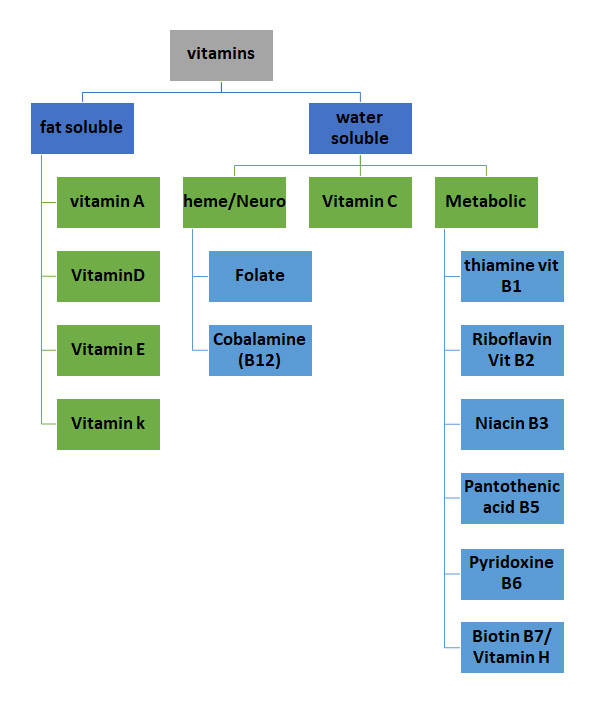
Fat soluble vitamins
Vitamin A
| Active form | Sources | Functions | Deficiency | Toxicity |
| Retinal Retinoic acid | spinach, kale, carrots, liver, kidney, fish, eggs, butter | Vision, Gene transcription, Tissue maintenance and cell differentiation, Antioxidant | Night blindness Retinopathy Xerophthalmia Keratomalacia Bitot spots, Keratinizing squamous metaplasia, immunosuppression poor growth  |
Acute toxicity - Nausea, vomiting, Vertigo, Fatigue,Headache, Blurred vision
Chronic toxicity - Alopecia, Arthralgia , Dry skin, scaling, Hepatosplenomegaly, hepatic toxicity, Pseudotumor cerebri Teratogenic effects are also seen. |
Vitamin D
| Active form | Sources | Functions | Deficiency | Toxicity |
| 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D | mushrooms, fortified foods, Synthesized in the skin when exposed to UV light | Increases Absorption of calcium and phosphate in the intestine, ↑ Reabsorption of calcium in the kidneys ,bone mineralization and remodelling | Osteomalacia in adults, Rickets in kids, Hypocalcaemia (tetany symptoms)
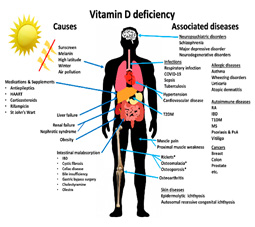 |
Granulomatous disorders, hypercalcemia, Loss of appetite |
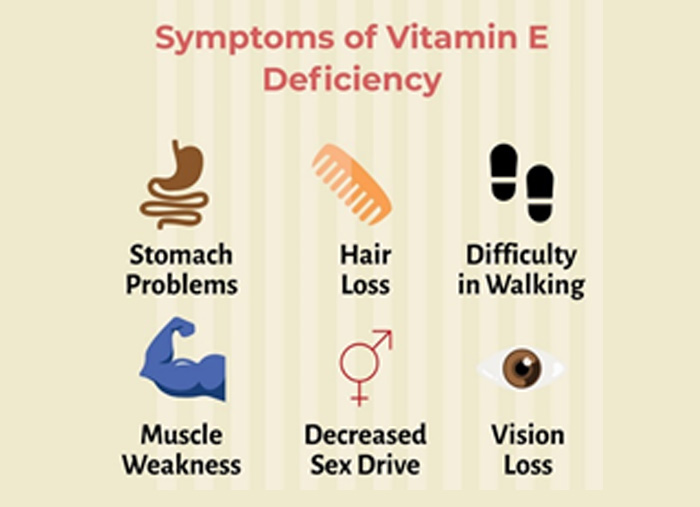
Vitamin E
| Active form | Sources | Functions | Deficiency | Toxicity |
| Tocopherol | meat, eggs, vegetable oils, leafy vegetables | Antioxidant property, Prevents haemolytic anaemia, prevents toxicity of liver, gonads germinal layer protection | Decreased Male fertility, encephalomalacia, muscular dystrophy,
 |
Necrotising enterocolitis in infants, alteration of vitamin k metabolism, |
Vitamin K
| Active form | Sources | Functions | Deficiency | Toxicity |
| hydroqunone | Leafy green vegetables (vitamin K1) Eggs, dairy, and meat (vitamin K2) Synthesized in small amounts by intestinal bacteria | Post translational modification of 2,7,9,10 blood clotting factors | Prolonged clotting time, Liver toxicity, Vitamin k antagonist, Haemorrhage, Vitamin k deficiency bleeding
 |
Over supplementation can cause jaundice, Kernicterus in infants, Haemolytic anaemia |
Water soluble vitamins
Vitamin B1
| Active form | Sources | Functions | Deficiency | Toxicity |
| thiamine pyrophosphate | Yeast, pork, legumes, whole grain cereal | Carbohydrate & amino acid metabolism, Acetylcholine synthesis, Transmission of nerve impulse. | Dry beriberi / peripheral neuritis Wet beriberi / cardiac manifestations Cerebral /Wernicke’s encephalopathy with korsakoff’s psychosis
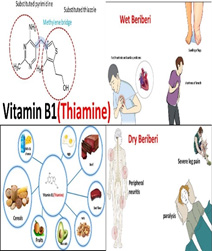 |
Excess amount are excreted via urine. Insomnia, headache, Drowsiness, hypersensitivity are possible. |
Vitamin B2
| Active form | Sources | Functions | Deficiency | Toxicity |
| Flavin mononucleotide | meat, fish, eggs, milk, green vegetables, yeast | FAD & FMN are cofactors involved in redox reactions. Succinate dehydrogenase in TCA cycle , Glutathione reductase in erythrocytes | Cheilitis, glossitis, Seborrheic dermatitis, corneal vascularization,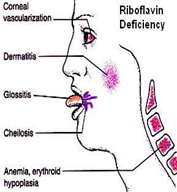 |
Excess amount are excreted via urine. |
Vitamin B3
| Active form | Sources | Functions | Deficiency | Toxicity |
| Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide Synthesized from tryptophan | meat (liver), cereals, seeds, legumes | Cofactor for redox reactions | Pellagra, bald tongue of sand with, raw beefy tongue, profuse salivation
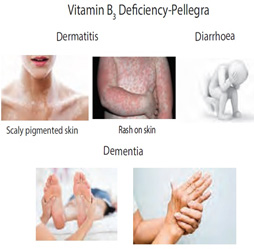 |
Excess amount are excreted via urine. Facial flushing, podagral, Hyperglycaemia, Hyperuricemia |
Vitamin B5
| Active form | Sources | Functions | Deficiency | Toxicity |
| Pantothenic acid | Liver, kidney, egg yolks, broccoli, milk | Essential component for co-enzyme (Pantothenic acid + ADP+ cysteine Cofactor for fatty acid, cholesterol | Burning feet syndrome.
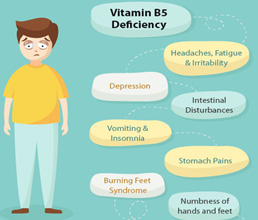 |
----- |
Vitamin B6
| Active form | Sources | Functions | Deficiency | Toxicity |
Pyridoxal phosphate |
nuts, whole grains, vegetables, yeast, meat | PLP is co enzyme for Transamination Decarboxylation Amino acid metabolism Glycogenolysis Involved in the synthesis of heme, histamine, niacin, Glutathione, cystathionine and neurotransmitters |
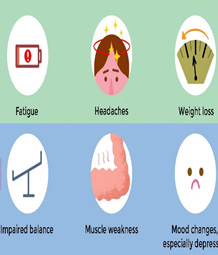 |
Dizziness, |
Vitamin B7
| Active form | Sources | Functions | Deficiency | Toxicity |
| Biotin | Soy products, nuts ,eggs and synthetized by microbial flora | Coenzyme for carboxylase reactions Fatty acid synthesis, fatty acid reduction, citric acid cycle, gluconeogenesis | Uncommon as its well distributed in food
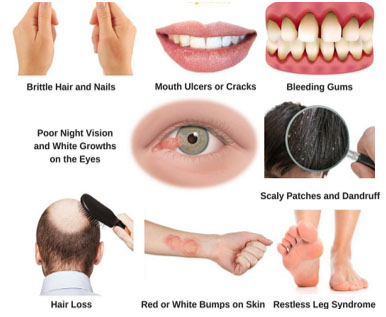 |
Not known |
Vitamin B9
| Active form | Sources | Functions | Deficiency | Toxicity |
| Tetrahydrofolic acid | Leafy green vegetables, fortified foods Small amounts are synthesized in intestinal flora | Required for amino acid ( glycine, serine ), purines and pyrimidines synthesis | Macrocytic Anaemia, glossitis, spina bifida during foetus development
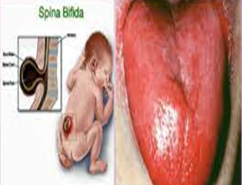 |
unknown |
Vitamin B12
| Active form | Sources | Functions | Deficiency | Toxicity |
| methyl cobalamin and adenosylcobalamin (Erythrocyte maturation factor) | Only intestinal microorganism and animals can produce it. | Co factor for enzymes : Methionine synthase, Methyl malonyl – CoA mutase | Pernicious anaemia, Autonomic Dysfunction, Myelin sheath, posterior, lateral tracts of spinal cord & peripheral nerves degeneration can cause neurologic problems, hunter’s glossitis / Moeller’s glossitis, beefy red tongue.

|
Nontoxic unless large amount is consumed. Pruritis, Urticaria, Anaphylaxis, Contact dermatitis. |
Vitamin C
| Active form | Sources | Functions | Deficiency | Toxicity |
| ascorbate | fruits and vegetables | Antioxidant, Promotes Iron absorption, Co enzymes for enzymatic reactions for collagen and nor adrenaline synthesis. | Scurvy, Delayed wound healing, cork screw hair pattern, trummer field zone – histologic features of bone in scurvy.
Woody legs & spontaneous bruises in lower extremities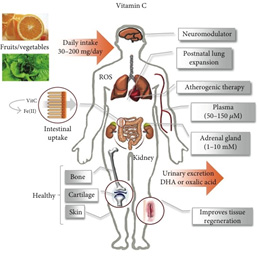 |
Nephrolithiasis, Increase in risk of iron absorption, Nausea, bloating, diarrhoea |
MCQs
1. Tocopherol is associated with
a) Vitamin Ab) Vitamin E
c) Vitamin K
d) Vitamin D
Answer: B
Vitamin E (also known as tocopherol or alpha-tocopherol) is a type of antioxidant, a substance that protects cells from damage. It helps your nerves and muscles work well, prevents blood clots, and boosts the immune system
Related posts
April 10, 2025
April 9, 2025
April 4, 2025




